
Wildlife Tourism Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Group (Groups/Friends, Couples, Family, and Solo); By Booking Mode; By Wildlife Tour Type; By Region; Segment Forecast, 2023 - 2032
- Published Date:Mar-2023
- Pages: 118
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM3079
- Base Year: 2022
- Historical Data: 2019-2021
Report Outlook
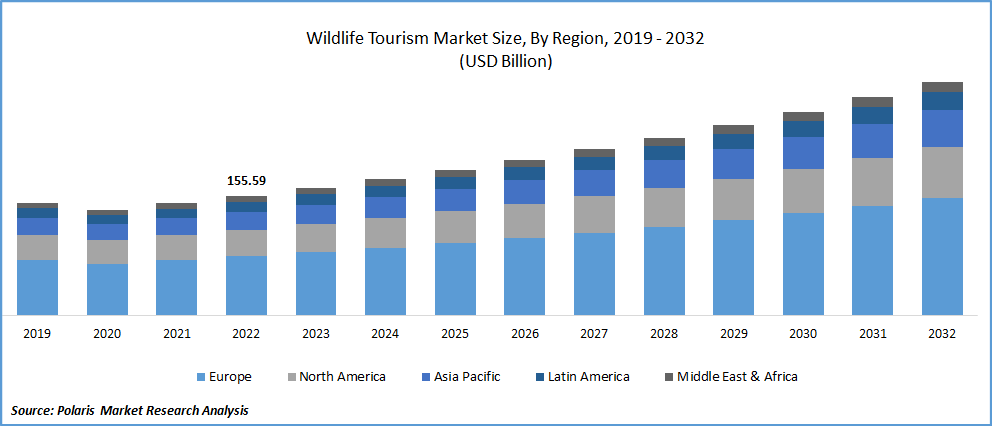
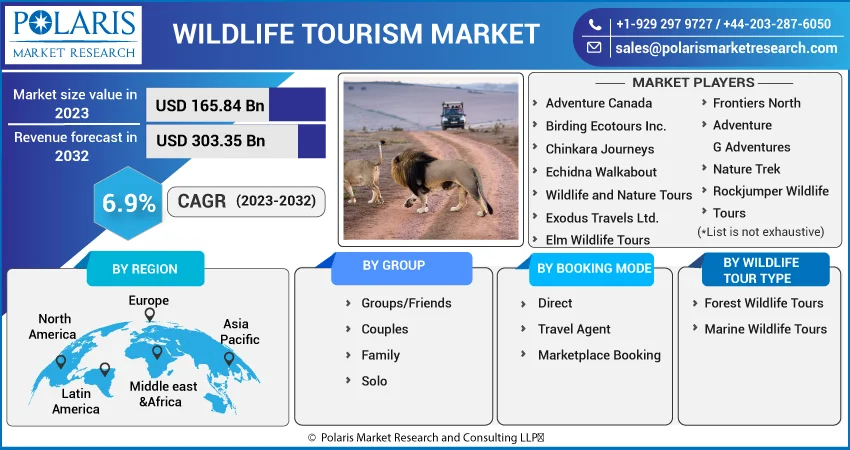
The global wildlife tourism market was valued at USD 155.59 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.9% during the forecast period. Wildlife tourism describes travel that focuses on observing and interacting with various animal species while traveling. Three specialized niche markets for wildlife tourism exist, along with corresponding interest groups. Non-consumptive tourism includes activities for observing animals, such as safaris, marine life viewing, and wildlife viewing. Non-consumptive travel only involves seeing and taking pictures of wild creatures living in their natural environment. Consumptive wildlife tourism is interfering with wildlife's ability to operate naturally through the use of practices like fishing, shooting, and horseback riding. These wildlife tourism niches have a high likelihood of endangering wild creatures and their habitat.
Know more about this report: Request for sample pages
The factor that is propelling the growth of the market is the rising visits for tourism activities which have assisted the development of wildlife sanctuaries and the preservation of animals due to the fees collected from tourism visits. Tourists who understand that the money they pay for admission goes toward the preservation of species are willing to return to wildlife sanctuaries and are even willing to pay more to do so. Visitors are educated about various fauna and flora species, which promotes the expansion of the wildlife tourism industry.
In addition to the ability to see animals, near the area wildlife sanctuaries now have a variety of hotels, guesthouses, eco-tourism villages, and jungles. Promoting wildlife tourism helps to conserve species and habitats, promote wildlife-based economies, fight wildlife crime, and decrease demand for illegal wildlife items. Important organizations like the World Bank are interested in its development. As a result, people are visiting national parks and wildlife sanctuaries for relaxation rather than the hustle and bustle of city life, which is generating lucrative possibilities for the global market.
Even though this money is set aside for conservation activities, there are some unfavorable effects as well. Tourists have been known to disrupt wildlife when they get very close to it to take pictures, and they may even have an impact on an animal's breeding cycle if they persistently request to take pictures of an animal in its mother's arms.
The COVID-19 outbreak has severely hurt the industry. However, this specialist sector is anticipated to rebound more quickly than others because wildlife tourism demands spacious locations. The biggest source nations for wildlife tourism in Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific are the United Kingdom, the US, India, Australia, Germany, and France. The demand for sustainability is rising as people learn more about the current climate problem. Following COVID-19, there will be a large market for wildlife tourism in the world, as more people seek out eco-friendly vacation options and desire to get closer to nature.
Know more about this report: Request for sample pages
Industry Dynamics
Growth Drivers
The neighboring locations used for filming movies and other projects draw local tourists, which promotes brisk growth in the wildlife tourism industry. The increased awareness of endangered species brought on by TV documentaries and media coverage is a major factor influencing the demand for wildlife tourism market. Visiting friends and family is another market where travel is done but to a smaller extent. The largest single category of wildlife tourism globally is bird viewing, one of its sub-segments. The fastest-growing type of wildlife tourism worldwide is whale watching. One of the few truly wild places on Earth is the ocean, and animal hotspots like the arctic regions can be reached by wildlife cruising.
Additionally, because it is in society's best interest to preserve wildlife to generate a sustainable income and because it increases tourists' commitment to conservation, wildlife tourism is becoming more and more significant to conservation efforts. Kenya may be the world's most well-known wildlife tourism destination among places to visit.
Expanding government programs, such as the UNWTO project for the conservation of the wild-life areas & the promotion of the sustainable tourism in the Africa & APAC region, are anticipated to spur industry expansion in the upcoming years. To familiarize children with the flora and animals in the parks, many schools also plan field trips to wildlife parks. The market for wildlife tourism is strongly supported by the frequent visits of wildlife photographers to the parks.
Report Segmentation
The market is primarily segmented based on the group, booking mode, wildlife tour type, and region.
|
By Group |
By Booking Mode |
By Wildlife Tour Type |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
Know more about this report: Request for sample pages
Solo Trips segment is expected to witness the fastest growth
The possibility of meeting like-minded individuals is one of the major advantages of traveling solo. These groups frequently have a mix of singles and couples. The number of single travelers surged when the global lockdowns were lifted. 60% of consumers on excursions are solitary travelers, according to Explore Worldwide Ltd., an adventure travel agency. The idea of solo travel will continue to spread and have an impact on the industry in the future as the digital nomad culture expands globally.
The majority of households travel abroad at least once a year, making tourists seasoned travelers. They become knowledgeable and demanding travelers as a result. The age range of wildlife tourists is not predetermined, making them a fairly diverse group. Because they make greater wages, the majority of educated wildlife tourists tend to spend more money. Further, they like taking vacations together or with their families. People are drawn to traveling in more together settings because it makes for a more memorable and superior experience.
Some tourists prefer to travel independently, which means they will make travel plans as they go and will not use the pre-arranged travel services provided by tour operators. Business travelers like animal activities as well, however, it is not their primary reason for traveling. As a result, this final group is primarily drawn to shore excursions (1-3 days).
Marine Wildlife Tours segment industry accounted for the highest market share in 2022
The marine wildlife tours segment is anticipated to hold the highest share which is driving the growth of the market. Travelers can canoe, kayak, or take a river cruise, among other activities, to observe animals from the water. Most tourists will find it appealing to employ native transportation, like a mokoro, which is used in various African nations, which will increase demand for wildlife tourism.
The Marketplace booking segment industry accounted for the largest market share in 2022
During the projected period, the marketplace booking sector is anticipated to have the maximum share. This might be ascribed to the comfort, accessibility of a wide range of options, and discounts provided to the traveler by such portals. Booking through a marketplace enables customers to compare different possibilities and provides all the necessary details so they can make an informed decision at any time and from any location. These elements will support the development of this market segment.
The demand in Asia-Pacific is expected to witness significant growth
According to UNWTO figures, outbound passengers from Asia and the Pacific make up 37.0% of all travelers worldwide, and regional spending on international travel has increased. The value of flora and fauna as well as growing awareness of global warming are driving the wildlife tourism industry in this area. Ranthambore Sanctuary & Kanha National Park are the 2 of the where visitors can encounter tigers up close. Tigers are a significant component of many wildlife sanctuaries. Global wildlife tourism is increasing as a result of the large number of visitors that come to these sanctuaries just to see tigers.
The welfare of wildlife is a growing issue for European tourists, who are even willing to pay more to see animals in the wild rather than in zoos. Animals used for entertainment are becoming more and more objectionable to them. It is deemed undesirable to feed animals or train them to perform tricks because it goes against their innate behavior and is bad for their welfare. One activity that Europeans are finding less and less appropriate is swimming with dolphins.
During the anticipated years, the Middle East & Africa regional market is anticipated to grow at the fastest rate. There are many tourist destinations in Africa, including the Serengeti National Park, the Masai Mara Nature Reserve, the Kruger National Park, and the Ngorongoro Crater Park. As more people become aware of the poaching of elephants and rhinos, tourism in the continent is growing as well as efforts to save the endangered species.
Competitive Insight
Key players in the wildlife tourism market include Absolute Zambia Safaris, Adventure Canada, Birding Ecotours, Rockjumper Wildlife Tours, Chinkara Journeys, Elm Wildlife Tours, Frontiers North Adventure, G Adventures, Nature Trek, and WildTrails Technologies.
Recent Developments
- In November 2022, G Adventures has made a sizeable financial investment in the restorative travel technology start-up, Reforest, intending to start to act through tree-planting. Reforest, an online network with a basis in Brisbane, Australia, links tourists with regional groups that are actively implementing reforestation to rebuild their ecosystems.
Wildlife Tourism Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2023 |
USD 165.84 billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2032 |
USD 303.35 billion |
|
CAGR |
6.9% from 2023 - 2032 |
|
Base year |
2022 |
|
Historical data |
2019 – 2021 |
|
Forecast period |
2023 - 2032 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2023 to 2032 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Group, By Booking Mode, By Wildlife Tour Type, By Region |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies |
Absolute Zambia Safaris Ltd., Adventure Canada, Birding Ecotours Inc., Chinkara Journeys, Echidna Walkabout Wildlife and Nature Tours, Exodus Travels Ltd., Elm Wildlife Tours, Frontiers North Adventure, G Adventures, Nature Trek, Oryx Worldwide Photographic Expeditions, Rockjumper Wildlife Tours, and WildTrails Technologies Pvt Ltd |
FAQ's
The wildlife tourism market report covering key segments are group, booking mode, wildlife tour type, and region.
Wildlife Tourism Market Size Worth $303.35 Billion By 2032.
The global wildlife tourism market expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.9% during the forecast period.
Asia-Pacific is leading the global market.
Key driving factor in wildlife tourism market are increased awareness of endangered species brought on by TV documentaries and media coverage
