
Waste to Energy Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report: By Technology (Thermal and Biological), Application, Waste Type, and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa) – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Feb-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM3132
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Waste to Energy Market Overview
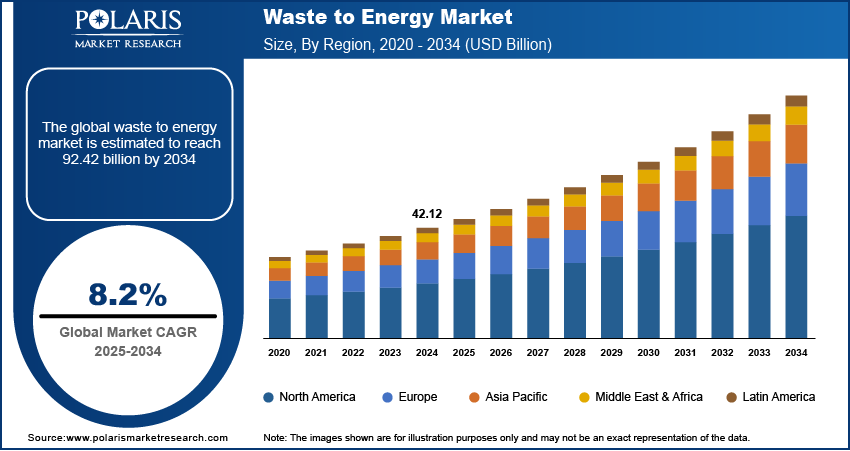
The global waste to energy market size was valued at USD 42.12 billion in 2024. The market is projected to grow from USD 45.51 billion in 2025 to USD 92.42 billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.2% from 2025 to 2034.
The global waste-to-energy (WTE) market focuses on the conversion of municipal solid waste (MSW), industrial waste, and other forms of waste into usable energy, including electricity, heat, or fuel. The market addresses environmental concerns and energy shortages by adopting technologies such as thermal (incineration, pyrolysis, and gasification) and biological processes (anaerobic digestion).
The increasing volume of waste generated globally is propelling the waste to energy market growth.According to International Finance Corporation, the world generates over 2 billion tons of municipal solid waste annually, and this is expected to increase by 70 percent by 2050. Traditional waste disposal methods, such as landfilling, are becoming unsustainable due to limited land availability and the environmental hazards associated with methane emissions and groundwater contamination. WTE technologies address these challenges by providing an efficient way to process large volumes of waste while generating valuable energy in the form of electricity, heat, or fuels. This dual benefit, reducing landfill dependency and contributing to renewable energy production, makes WTE a critical solution for modern waste management.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The waste to energy market demand is driven by rising stringent environmental regulations globally. Governments worldwide are implementing policies and initiatives to curb greenhouse gas emissions, minimize environmental pollution, and promote renewable energy sources. For instance, regulations such as the European Union's Landfill Directive impose restrictions on the amount of biodegradable municipal waste sent to landfills, encouraging alternative disposal methods such as waste to energy. Similarly, carbon pricing and landfill taxes in several countries make traditional waste disposal methods less economically viable, positioning WTE as a cost-effective alternative and driving market expansion.
Waste to Energy Market Dynamics
Growing Urbanization Worldwide
Urban areas, which reside over 56% or 4.4 billion of the global population according to World Bank, are significantly contributing to the expansion of waste production due to higher consumption patterns, industrial activities, and infrastructural developments. This surge in waste generation places immense pressure on traditional disposal methods such as landfills, which are not only space-constrained but also pose severe environmental and health risks. Waste to energy emerges as an effective solution to manage the growing waste volumes in urban settings, as it reduces landfill dependency while simultaneously generating energy to meet the rising power demands of expanding cities. Additionally, governments and municipalities are increasingly investing in WTE facilities to tackle urban waste challenges efficiently, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and ensure sustainable urban development. Thus, the rising urbanization globally is fueling the waste to energy market growth.
Advancement in Waste-to-Energy Technologies
Innovative waste to energy technologies have significantly improved efficiency, reducing costs and minimizing environmental impact. Advanced gasification and pyrolysis systems now allow for higher energy recovery rates with lower emissions, making WTE a viable alternative to traditional energy sources. The development of small-scale modular WTE plants has expanded accessibility to rural and semi-urban areas, where waste management infrastructure is often inadequate. These advancements are contributing to the waste to energy market expansion.

Waste to Energy Market Segment Insights
Waste to Energy Market Evaluation by Waste Type Insights
Based on waste type, the waste to energy market is categorized into municipal solid waste, industrial waste, and agricultural waste. The municipal solid waste segment held the largest waste to energy market share in 2024 due to the rapid increase in urban population and shifts in consumption patterns, particularly in developing and densely populated countries. Urban areas generate significant amounts of household waste, pushing governments and private entities to adopt advanced waste management solutions, such as waste to energy. Investments in integrated municipal waste systems and growing support for circular economy initiatives, especially in Europe and Asia, have also contributed to the dominance of the segment.
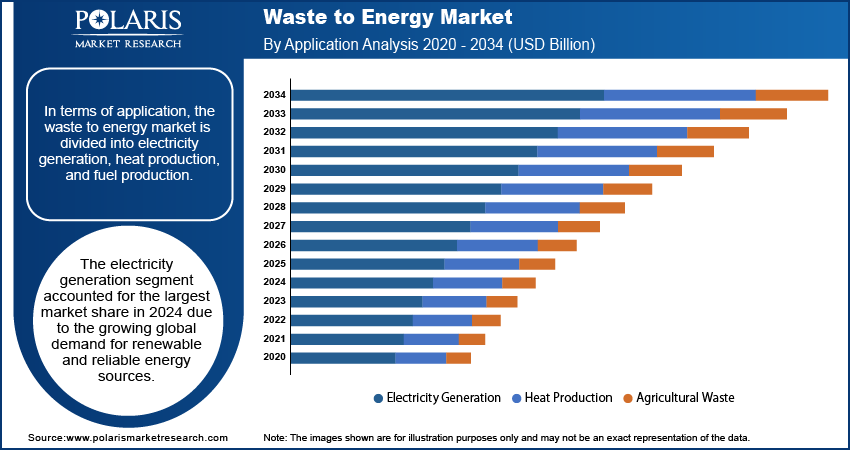
Waste to Energy Market Assessment by Application Insights
In terms of application, the waste to energy market is divided into electricity generation, heat production, and fuel production. The electricity generation segment accounted for the largest market share in 2024 due to the growing global demand for renewable and reliable energy sources. Urbanization and industrialization have significantly increased electricity consumption, creating a need for alternative power generation methods such as waste to energy that reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, governments and organizations worldwide have prioritized the integration of waste to energy into national grids, supported by policies such as feed-in tariffs, renewable energy subsidies, and tax benefits.
Waste to Energy Market Regional Analysis
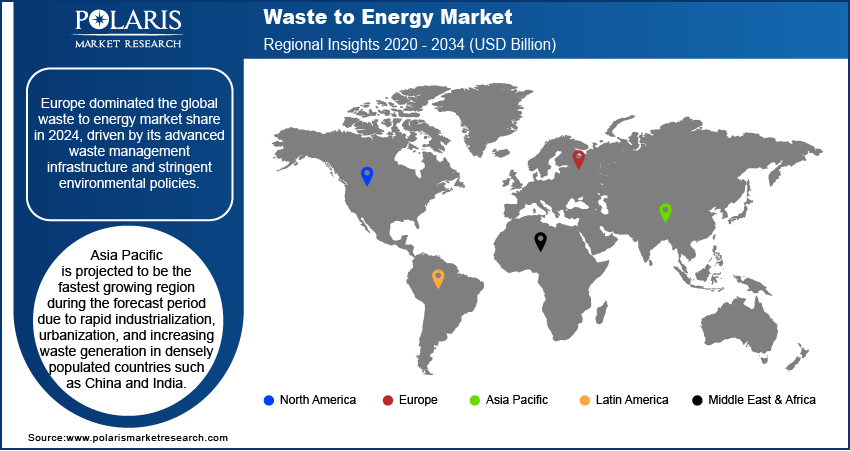
By region, the report provides the waste to energy market insights into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. Europe dominated the global waste to energy market share in 2024, driven by its advanced waste management infrastructure and stringent environmental policies. Countries in the region, such as Germany, Sweden, and the Netherlands, have implemented comprehensive frameworks to reduce landfill dependency and promote energy recovery solutions. Germany led the region due to its well-established waste processing facilities, government-backed subsidies for renewable energy, and strict regulations under the European Union’s Waste Framework Directive. These measures encourage sustainable practices by imposing high landfill taxes and incentivizing energy recovery projects. Additionally, public awareness and high recycling rates have strengthened the region's ability to efficiently divert waste into energy recovery systems, contributing to its dominance in the global market.
Asia Pacific is projected to register the fastest growth during the forecast period due to rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing waste generation in densely populated countries such as China and IndiaAccording to data published by the Asian Development Bank, more than 55% of Asia's population was projected to be urban by 2023. Governments in this region are making significant investments in modern waste management technologies to address growing environmental challenges and rising energy demand. China dominates the region with its large-scale adoption of advanced energy recovery systems, supported by government initiatives such as subsidies for green energy projects and strict regulations on waste disposal. The country has further established numerous facilities to process municipal and industrial waste efficiently, reducing environmental impact while contributing to the national energy supply. India is also experiencing rapid growth in this market, with efforts to improve urban infrastructure and reduce reliance on fossil fuels through energy recovery solutions.
Waste to Energy Market – Key Players and Competitive Insights
Major market players are investing heavily in research and development in order to expand their offerings, which will help the waste to energy market grow even more. These market participants are also undertaking a variety of strategic activities to expand their global footprint, with important market developments including innovative launches, international collaborations, higher investments, and mergers and acquisitions between organizations.
The waste to energy market is fragmented, with the presence of numerous global and regional market players. Major players in the market include Hitachi Zosen Inova AG; Suez; Covanta Holding Corporation; China Everbright International Limited; Veolia; Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC; Ramboll Group A/S; Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc.; Wheelabrator Technologies Inc.; and Xcel Energy Inc.
Hitachi Zosen Inova AG (HZI), based in Zurich, Switzerland, is a prominent player in the waste-to-energy (WTE) market, specializing in converting waste into energy through advanced technologies. Established in 1933 as a spin-off of the Ludwig von Roll company, HZI has evolved significantly over the decades, particularly after its acquisition by the Japan-based Hitachi Zosen Corporation in 2010. This strategic move enabled HZI to leverage Hitachi's extensive technological expertise and resources, enhancing its capabilities in energy recovery and environmental sustainability. HZI operates as a comprehensive solution provider in the energy transition and circular economy landscape, focusing on WTE and renewable gas technologies. The company is involved in all stages of project development, serving as a technology supplier, engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) contractor. HZI’s portfolio includes the design and implementation of thermal and biological waste recovery systems.
Suez, headquartered in Paris, France, is a global utility company specializing in water and waste management. Suez has established itself as a crucial player in the environmental services sector, focusing on sustainable practices and innovative solutions to address the challenges of waste disposal and resource recovery. The company operates across various continents, providing essential services to municipalities and industries while emphasizing the principles of the circular economy. Suez's operations encompass a wide range of activities, including water distribution and treatment, wastewater management, recycling, and waste recovery, which includes hazardous waste management. Suez has made significant advancements by developing technologies that convert municipal solid waste into energy, significantly reducing landfill waste and generating renewable energy. This process contributes to energy security and supports sustainable development goals.
List of Key Companies in Waste to Energy Market
- Hitachi Zosen Inova AG
- Suez
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- China Everbright International Limited
- Veolia
- Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC
- Ramboll Group A/S
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc.
- Wheelabrator Technologies Inc.
- Xcel Energy Inc.
Waste to Energy Industry Developments
January 2025: The U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) and Vehicle Technologies Office (VTO) announced USD 6.9 million in funding for nine projects aimed at supporting local waste-to-energy management solutions for transportation energy needs.
November 2024: Union Home and Cooperation Minister of India, Shri Amit Shah, inaugurated a waste-to-energy plant in Ahmedabad as a step towards a Clean Ahmedabad.
Waste to Energy Market Segmentation
By Technology Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Thermal
- Incineration
- Pyrolysis
- Gasification
- Biological
- Anaerobic Digestion
By Application Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Electricity Generation
- Heat Production
- Fuel Production
By Waste Type Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Municipal Solid Waste
- Industrial Waste
- Agricultural Waste
By Regional Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Waste to Energy Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2024 |
USD 42.12 billion |
|
Market Forecast Value in 2025 |
USD 45.51 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 92.42 billion |
|
CAGR |
8.2% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
• The global waste to energy market size was valued at USD 42.12 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 92.42 billion by 2034.
• The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 8.2% during the forecast period.
• Europe had the largest share of the global market in 2024.
• Some of the key players in the market are Hitachi Zosen Inova AG; Suez; Covanta Holding Corporation; China Everbright International Limited; Veolia; Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC; Ramboll Group A/S; Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc.; Wheelabrator Technologies Inc.; and Xcel Energy Inc.
• The municipal solid waste segment dominated the waste to energy market in 2024.
