
Thalassemia Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report, By Treatment Type (Iron Chelating Drugs, Blood Transfusions, Folic Acid Supplements, Gene Therapy, Others); By End-Use; By Disease Type; By Region; Segment Forecast, 2022 - 2030
- Published Date:Oct-2022
- Pages: 117
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM1377
- Base Year: 2021
- Historical Data: 2018 - 2020
Report Outlook
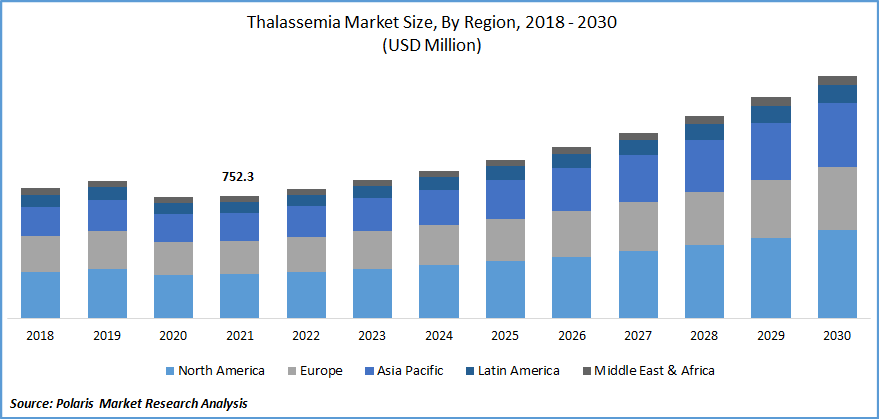
The global Thalassemia market was valued at USD 752.3 million in 2021 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.2% during the forecast period. Some of the drivers projected to drive the global market are increased awareness, technological breakthroughs such as stem cell treatment, growth in health care expenditure, and a potential portfolio. Furthermore, increasing investments in R&D initiatives by biotechnology and pharmaceutical businesses are driving market expansion.
Know more about this report: Request for sample pages
Thalassemia is a genetic blood condition in which the human body produces an abnormal kind of hemoglobin. It causes a huge number of blood cells to be destroyed, resulting in anemia. Thalassemia is a genetic condition caused by the deletion or modification of a specific gene segment. If only one parent carries the gene, the child may get thalassemia mild. If both parents are chronic carriers, the child may acquire a severe version of the disease.
The disease is classified into three types: beta, alpha, and minor. The degree and kind of condition determine how it is treated. The body cannot generate beta globulin in beta-thalassemia. Patients having beta and alpha thalassemia have more serious symptoms than those with thalassemia mild. Common symptoms include bone abnormalities, black urine, pale complexion, and extreme weariness.
Governments around the world to combat the COVID-19 outbreak, from vaccine research to planning for drug supply chain issues. Approximately 115 vaccine candidates and 155 compounds are now in the R&D pipeline. In May 2020, The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued new recommendations noting that patients with hemoglobin disorders, such as thalassemia and sickle cell disease, may be more vulnerable to COVID-19-related sickness.
Furthermore, commonly used drugs like hydroxychloroquine have witnessed a significant increase in demand for COVID-19 management. As many affluent countries face a shortage of these medications, the increased demand for COVID-19 management drugs has created enormous potential for businesses.
As a result of the increased demand for COVID-19 vaccines and treatment medications, the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are predicted to grow significantly in the future. This will, in turn, have a considerable impact on the thalassemia market.

Know more about this report: Request for sample pages
Industry Dynamics
Growth Drivers
The rising product launches in the market are boosting the market growth over the forecast period. For instance, in May 2020, Luspatercept was suggested for authorization by the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) to treat anemia in both the rare blood condition beta type and the hematological malignancy myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
Also, in June 2021, Protagonist Therapeutics confirmed that the FDA has allowed New Drug Classification to its lead investigational new medication participant, rusfertide, for the therapy of individuals who has polycythemia vera for the decrease of erythrocytosis in each of those sick people who do not require further therapies for thrombocytosis and/or leukocytosis.
Furthermore, government measures to raise thalassemia awareness were expected to propel the market in the next years. For instance, in March 2022, CIL inked an MoU with the Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani for its primary program "Thalassemia Bal Seva Yojana," which would fund bone marrow transplants for Thalassemia and Alpastic Anaemia patients from low-income families. This yojana gives financial support of up to ten lakh rupees to children of low-income families suffering from Thalassemia and Aplastic Anaemia. This, in turn, is expected to have a significant impact on the worldwide market's growth throughout the forecast period.
Report Segmentation
The market is primarily segmented based on treatment type, disease type, end-use, and region.
|
By Treatment Type |
By Disease Type |
By End-Use |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
Know more about this report: Request for sample pages
Iron Chelating drugs segment is expected to witness fastest growth
Iron overload is the most common cause of disease in thalassemia patients. Iron overload occurs in non-transfused patients as a result of increased intestinal absorption of nutrients iron. Iron overload is a primary cause of death and organ damage. Phlebotomy and chelation are the two therapeutic options for eliminating excess iron. While phlebotomy is a highly successful method of iron removal, it is not recommended in patients with thalassemia however after bone marrow transplants.
Medications for the illness primarily address iron excess caused by blood transfusions, fetal hemoglobin, and indicaxanthin, for hemoglobin breakdown avoidance. If medications are in phase III trial pipeline, the market is likely to grow significantly. The market in developed regions is being driven by rising awareness of treatment modalities and the announcement of novel treatment approaches.
Furthermore, the large young population in emerging markets like India and Pakistan is expected to drive up demand for medications and treatments in the future years. During the forecast period, the segment is expected to rise at an exponential rate. The increasing frequency of patients and increased R&D expenditures are the primary reasons driving the segment's growth.
Beta thalassemia segment industry accounted for the highest market share in 2021
Beta thalassemia is a common hereditary condition in which the patient's body can not produce enough hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the component of red blood cells (RBCs) that send oxygen throughout the body. Anemia and other medical concerns such as weakness and breathing difficulties can result from aberrant hemoglobin. Symptoms of beta thalassemia can range from minor to severe, depending on the kind.
The growing number of beta type patients worldwide is expected to drive market expansion over the forecast period. Key market participants are concentrating on submitting applications for drug therapy approved for the treatment of beta type, which is projected to fuel growth in the global thalassemia market during the forecast period.
For instance, in September 2021, Bluebird Bio stated the beti-cel gene therapy for the diagnosis of beta type had already been properly accepted for approval in the United States. Beti-cel was evaluated as a one-time therapy for beta type, a rare disease that inhibits the formation of hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells, in many preliminary and delayed clinical trials.
Gene Therapy is expected to hold the significant revenue share
Gene therapy is considered to be extremely promising, with many genomic medicines in delayed trials. Currently, 15 pipeline medicines for the therapy of thalassemia are under clinical development. Most of these goods are based on gene delivery and attempt to cure the illness. The market research covers promising pipeline medications that are scheduled to be released throughout the projected period.
The demand in North America is expected to witness significant growth
The presence of important players, the higher incidence of thalassemia patients in the region, and the well-established healthcare infrastructure are key factors responsible for the industry's large share. Furthermore, positive government efforts and an increase in research partnerships are likely to fuel market growth. The United States has the largest percentage due to increased knowledge of the disorder, a growing proportion of people having thalassemia carriers gene, and a rise in fertility rates due to genetic heterogeneity.
In the Asia Pacific, there has been an upsurge in same-community marriage patterns and a high number of alpha type patients. Due to the tremendous heterogeneity, and an inconsistent frequency of heterozygotes or carriers, Asia-Pacific is expected to develop significantly. Furthermore, the government and numerous other groups are attempting to raise public awareness.
Governments in developing countries are making considerable expenditures on healthcare infrastructure and the life sciences industry, which is expected to expand access to healthcare. This is projected to raise the demand for cutting-edge technologies. Furthermore, governments and non-governmental organizations are launching campaigns in poor countries to raise public awareness for early detection. This increases the appeal of testing for diagnosis and, as a result, provides enormous market prospects.
Competitive Insight
Some of the major players operating in the global thalassemia market include ApoPharma Inc., Acceleron Pharma, Inc., Bluebird Bio Corporation, Bellicum Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Fresenius Kabi AG, GlaxoSmithKline plc, IONIS Pharmaceuticals, Kiadis Pharma, Lonza Group Ltd., La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company, Novartis AG, Pfizer, Inc., SG Pharma Pvt. Lmt., Sangamo Therapeutics, and Vifor Pharma
Recent Developments
In April 2021, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated and CRISPR Therapeutics declared a collaborative effort agreement to acquire, manufacture, and commercialize CTX001, an interventional CRISPR/Cas9-based genome-editing therapy being established as a potential therapeutic option for sickle cell disease (SCD) and transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia (TDT). Furthermore, CRISPR will get a $900 million initial payment, with the possibility of a USD 200 million reimbursement upon CTX001's first regulatory approval.
Thalassemia Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2021 |
USD 752.3 million |
|
Revenue forecast in 2030 |
USD 1,492.9 million |
|
CAGR |
8.2% from 2022 – 2030 |
|
Base year |
2021 |
|
Historical data |
2018 – 2020 |
|
Forecast period |
2022 – 2030 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2022 to 2030 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Treatment Type, By Disease Type, By End-Use, By Region |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Key Companies |
ApoPharma Inc., Acceleron Pharma, Inc., Bluebird Bio Corporation, Bellicum Pharmaceuticals, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Fresenius Kabi AG, GlaxoSmithKline plc, IONIS Pharmaceuticals, Kiadis Pharma, Lonza Group Ltd., La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company, Novartis AG, Pfizer, Inc., SG Pharma Pvt. Lmt., Sangamo Therapeutics, and Vifor Pharma |
