
Shore Power Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report: By Installation Type, Power Rating, Component, Connection (New Installation and Retrofit), and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa) – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Feb-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM3096
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Shore Power Market Overview
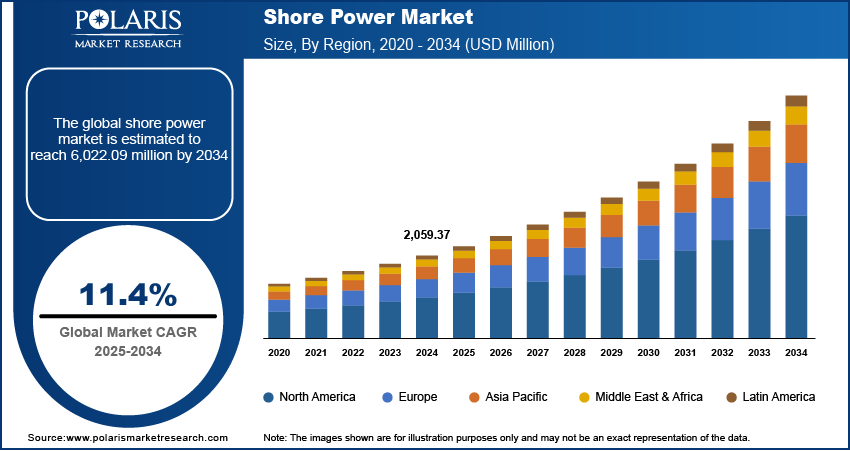
The global shore power market size was valued at USD 2,059.37 million in 2024. The market is expected to grow from USD 2,287.62 million in 2025 to USD 6,022.09 million by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 11.4% from 2025 to 2034.
Shore power refers to the infrastructure and technology that provides electrical power to vessels while they are docked in port, eliminating the need for onboard generators. This market plays a major role in reducing the environmental impact of shipping operations by allowing ships to shut down their auxiliary engines while in port, thereby reducing emissions and noise.
The global shore power market is growing due to increased regulatory pressure on the shipping industry to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and the rising demand for cleaner energy sources. A January 2025 report by the EU highlighted the FuelEU Maritime Regulation, which took effect on January 1, 2025. This regulation mandates a gradual reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) intensity for ships weighing over 5,000 gross tons that call at EU ports. The targets include a 2% reduction in GHG emissions by 2025, with an 80% reduction by 2050, compared to 2020 levels. Additionally, this regulation promotes the use of renewable and low-carbon fuels, and it requires ships to use onshore power supply (OPS) or zero-emission technologies while docked starting in 2030.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The tightening of environmental regulations globally is another key driver of the shore power market expansion. International maritime organizations, such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO), along with regional regulations, are pushing the shipping industry towards adopting shore power systems. The IMO has established strict limits on sulfur oxide (SOx) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from ships, leading ports to invest in shore power facilities to meet these requirements. These regulations aim to reduce air pollution in port cities, with a particular focus on carbon emissions and particulate matter from diesel-powered ships. The integration of shore power is thus seen as a crucial component in achieving these environmental goals. Moreover, port authorities and operators are investing in upgrading infrastructure to meet these standards, contributing to the overall market expansion.
Shore Power Market Dynamics
Increasing Maritime Traffic and Expanding Port Networks
Ports worldwide are experiencing higher ship turnaround times, which has increased the demand for sustainable infrastructure, including shore power. Shore power systems enable ships to connect to the grid, reducing reliance on onboard generators during port stays. Additionally, there is a heightened need for electrification and modernization to support larger ships and comply with environmental standards by expanding port networks. A May 2022 report by the EU highlighted the European Commission's REPowerEU plan, which facilitates the electrification of ports as part of a broader strategy to decarbonize transportation hubs. The plan includes binding targets for port electrification under the Alternative Fuels and Infrastructure Directive (AFIR) and aims to reduce vessel carbon intensities through innovative technologies. The adoption of shore power helps in reducing fuel consumption and emissions, aligning with the sustainability goals of modern port operations. As trade volumes continue to grow, the deployment of shore power solutions is becoming an integral part of future-ready port strategies, impacting the shore power market development favorably.
Growing Pollution Control Laws and Regulations
International and regional bodies, such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the European Union and others, have implemented strict requirements to limit sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon emissions from ships. A June 2024 report by the ICCT stated that shore power at the Port of Seattle could reduce CO2, NOx, and PM2.5 emissions by 68%, 85%, and 75% respectively. It could also lower PM2.5 concentrations by up to 83%, providing an estimated USD 27 million in annual public health benefits. These regulations compel shipping companies and port authorities to adopt cleaner technologies, including shore power, to achieve compliance. Shore power enables vessels to turn off their auxiliary engines while docked, eliminating harmful pollutants and reducing noise in port cities. The shore power market is gaining momentum as a practical and sustainable solution to meet these environmental mandates with increasing enforcement of such regulations, particularly in emission-controlled areas (ECAs).
Shore Power Market Segment Insights
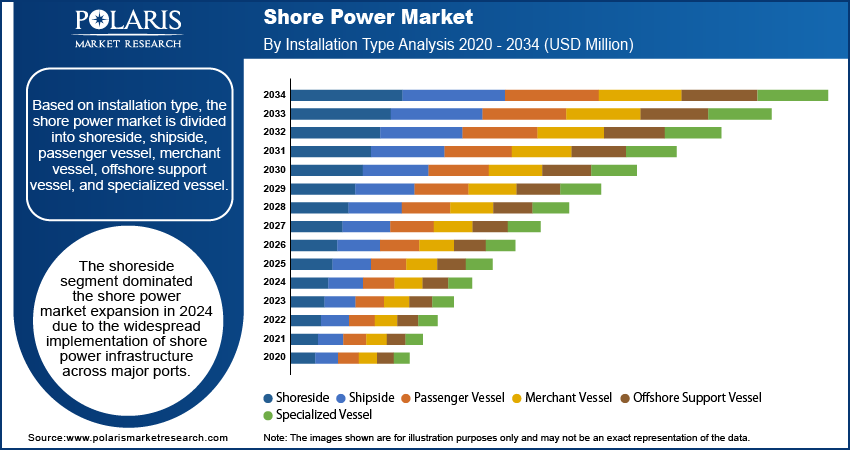
Shore Power Market Assessment by Installation Type Outlook
The global shore power market segmentation, based on installation type, includes shoreside, shipside, passenger vessel, merchant vessel, offshore support vessel, and specialized vessel. The shoreside segment dominated the market in 2024 due to the widespread implementation of shore power infrastructure across major ports. Increasing regulatory requirements for reducing emissions and noise pollution in port areas have led to significant investments in shoreside installations. Additionally, shoreside installations offer the advantage of centralized power distribution, ensuring seamless connectivity for diverse container types. Ports in Europe and North America, particularly those located in emission control areas (ECAs), played a pivotal role in the expansion of shoreside installations. The focus on sustainability and the integration of renewable energy sources into port grids has further boosted this segment's dominance.
Shore Power Market Evaluation by Connection Outlook
The global shore power market segmentation, based on connection, includes new installation and retrofit. The retrofit segment is expected to witness the fastest shore power market growth during the forecast period due to increasing demand for upgrading existing ships and port infrastructure to comply with strict environmental regulations. Shipping companies are increasingly opting for retrofitting solutions to improve the sustainability of their fleets without incurring the high costs of procuring new vessels. Additionally, government subsidies and incentives for adopting cleaner technologies are encouraging retrofitting projects. The flexibility and cost-effectiveness of retrofits make them particularly appealing in regions with established port infrastructure, such as Asia Pacific and Europe. This trend aligns with the growing global focus on reducing the environmental impact of maritime operations while optimizing operational efficiency.
Shore Power Market Regional Analysis
By region, the report provides the shore power market insights into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. Asia Pacific dominated the shore power market revenue in 2024 due to its extensive maritime trade activities, rapidly expanding port infrastructure, and stringent environmental regulations in key countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea. The region’s ports have been heavily investing in electrification to support increasing vessel traffic and comply with emission control standards, especially within emission control areas (ECAs). A June 2024 report by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) stated that India is expanding its shore power infrastructure at major ports to reduce diesel pollution and enhance public health. The initiative, part of the 'Harit Sagar Green Port Guidelines', aims for phased implementation by 2025, targeting a significant reduction in carbon emissions from port operations while promoting cleaner energy sources. Governments and port authorities in the region are actively promoting sustainable port operations, with considerable funding directed towards shore power installation projects. Additionally, Asia Pacific is home to some of the world’s busiest ports, such as Shanghai and Singapore, which have accelerated the adoption of shore power systems to address air pollution and improve operational efficiency. The combination of trade volume growth and regulatory enforcement has solidified Asia Pacific's leadership in the market.
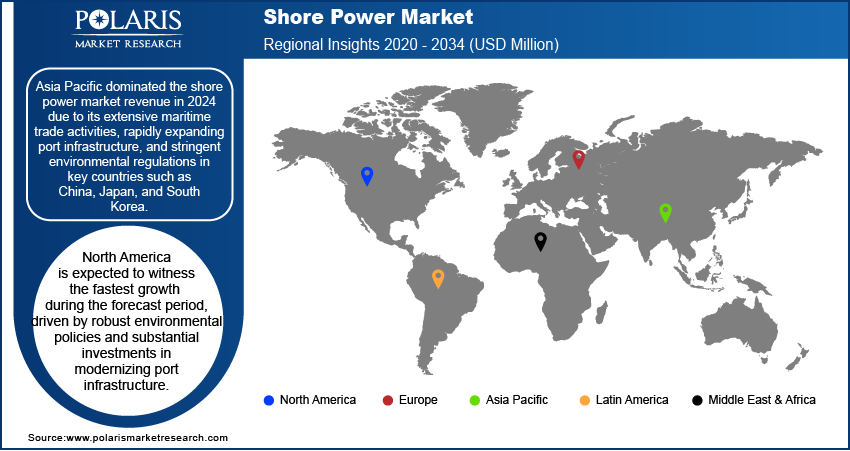
North America is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period, driven by robust environmental policies and substantial investments in modernizing port infrastructure. For instance, in November 2024, the US Department of Transportation’s Maritime Administration (MARAD) revealed plans to allocate nearly USD 580 million from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law for 31 port enhancement projects across 15 states and one US territory. The US and Canada, in particular, have implemented strict regulations to reduce maritime emissions, including mandates for shore power adoption in major ports such as Los Angeles, Long Beach, and Vancouver. The availability of government grants and incentives to support sustainable initiatives has further encouraged the implementation of shore power systems. Additionally, the region’s strong focus on innovation and technological advancement in electrification has positioned North America as a frontrunner in deploying next-generation shore power solutions. The increasing adoption of clean energy sources to power port grids has further amplified growth prospects, reflecting the region’s commitment to environmental sustainability and decarbonization.
Shore Power Market – Key Players and Competitive Insights
Major market players in the shore power market are investing heavily in research and development to expand their offerings, thereby driving market growth. The competitive landscape is intense, with leading players focusing on innovation, sustainability, and strategic partnerships to strengthen their market positions. Schneider Electric and Wärtsilä are leveraging advanced technologies to enhance energy efficiency and reduce emissions, while ABB is dominating with cost-effective modular shore power solutions tailored for emerging markets. Collectively, these companies hold a significant market share, driven by their efforts in regional expansions, integrating renewable energy sources into shore power systems, and advancing digitalization to optimize port operations. This strategic focus ensures their leadership in addressing the evolving environmental and operational needs of the maritime industry. A few key major players are ABB; AEG Power Solutions; BluEco; Cavotec SA; Danfoss; Eaton; Emerson Electric Co.; Engie; GE Grid Solutions; Konecranes; Powercon; Schneider Electric; Siemens; Wärtsilä.
ABB Ltd. is a Swedish-Swiss multinational corporation headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland, dual-listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange and the Nasdaq Nordic exchange. ABB specializes in electrification and automation solutions. It was formed in 1988 ABB operates in over 100 countries with approximately 110,000 employees. The company’s core activities include shore power generation, transmission, and distribution; industrial automation; and robotics. ABB is a technology leader, enabling a more sustainable and resource-efficient future. The company’s operations are organized into four global business areas, which are made of 21 divisions. ABB develops and sells products and system solutions to utilities, industries, channel partners, and original equipment manufacturers.
Eaton offers a range of products and solutions for shore power applications, focusing on delivering safe, reliable, and efficient power for marine operations. Their portfolio includes UL-listed pedestals that provide power to various sizes of watercraft, from motorboats to superyachts. Eaton's Crouse-Hinds series ship/shore connectors are designed for quick and safe connection and disconnection of docked ships to shore-generated power, meeting MIL-C-24368 standards and handling currents up to 500 amps per phase. Eaton also provides Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) solutions for marine applications, such as the 9PX Marine UPS and 9PHD Marine UPS, which are reliable and efficient UPS solutions suitable for a range of marine and offshore applications. These products ensure efficient and reliable power for onshore operations, maximizing safety and minimizing environmental impact. Eaton strengthens its design and engineering capabilities to provide customers with sustainable energy-saving solutions for marine and other industries.
List of Key Companies in Shore Power Market
- ABB
- AEG Power Solutions
- BluEco
- Cavotec SA
- Danfoss
- Eaton
- Emerson Electric Co.
- Engie
- GE Grid Solutions
- Konecranes
- Powercon
- Schneider Electric
- Siemens
- Wärtsilä
Shore Power Industry Developments
In August 2024, ERMA FIRST launched BLUE CONNECT, a high-voltage shore power solution that facilitates a vessel's connection to a port's electrical grid to power its systems while docked. This allows ships to switch off diesel generators, reducing noise and emissions.
In June 2024, The Port of Helsinki launched an onshore power supply system for Finnlines vessels, reducing port emissions by 50 to 80 percent.
Shore Power Market Segmentation
By Installation Type Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Shoreside
- Shipside
- Passenger Vessel
- Merchant Vessel
- Offshore Support Vessel
- Specialized Vessel
By Power Rating Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Up to 30 MVA
- 30-60 MVA
- Above 60 MVA
By Component Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Transformers
- Switchgear Devices
- Frequency Converter
- Cables and Accessories
- Others
By Connection Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- New Installation
- Retrofit
By Regional Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Shore Power Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2024 |
USD 2,059.37 million |
|
Market Size Value in 2025 |
USD 2,287.62 million |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 6,022.09 million |
|
CAGR |
11.4% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
• The global shore power market size was valued at USD 2,059.37 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 6,022.09 million by 2034.
• The global market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.4% during the forecast period.
• Asia Pacific dominated the global market in 2024.
• A few of the key players in the market are ABB; AEG Power Solutions; BluEco; Cavotec SA; Danfoss; Eaton; Emerson Electric Co.; Engie; GE Grid Solutions; and Konecranes.
• The shoreside segment dominated the market in 2024.
