
Refrigerant Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report: By Type (Fluorocarbons, Hydrocarbons, and Inorganic Refrigerants), Application, and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa) – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Dec-2024
- Pages: 120
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM1609
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Refrigerant Market Overview
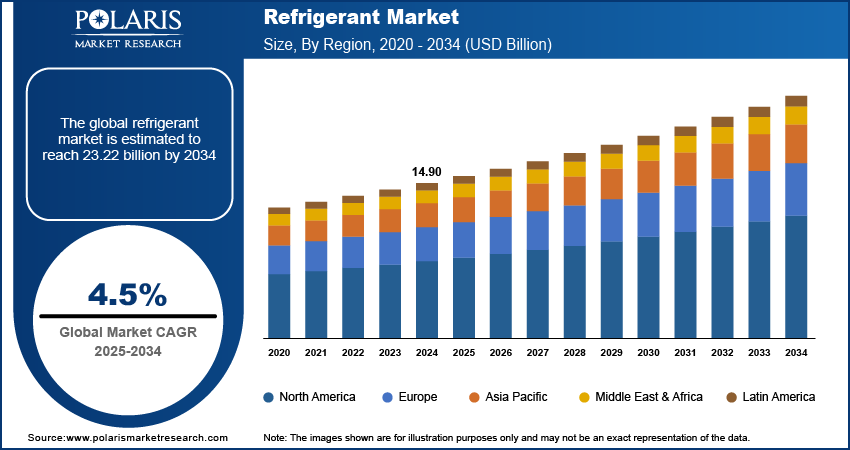
The global refrigerant market size was valued at USD 14.90 billion in 2024. The market is projected to grow from USD 15.56 billion in 2025 to USD 23.22 billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 4.5% during 2025–2034.
The global refrigerant market refers to the industry that produces and supplies chemicals used in cooling systems, such as air conditioning, refrigeration, and heat pumps. These refrigerants play a critical role in maintaining temperature control in various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. The market growth is driven by factors such as the growing demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly cooling solutions, the shift toward low-global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants, and increasing regulatory pressure to phase out ozone-depleting substances. Additionally, refrigerant market trends such as the rise of advanced cooling technologies, including smart refrigeration systems, and the expansion of the HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) industry would contribute to the market growth.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Refrigerant Market Trends
Shift Toward Low-GWP Refrigerants
A significant trend in the global refrigerant market is the growing transition to low-global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants. As environmental concerns increase, governments and industries are focusing on reducing the impact of refrigerants on climate change. The Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol, which aims to phase out hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), has been a key driver of this shift. The European Union's F-gas regulation and the United States’ American Innovation and Manufacturing (AIM) Act are pushing for the adoption of alternatives with a lower GWP, such as natural refrigerants (CO2 and ammonia) and HFOs (hydrofluoroolefins). According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the reduction in HFC usage will help mitigate the release of high-GWP refrigerants, ultimately preventing up to 0.5°C of global temperature rise by 2100. This transition is becoming more vital as businesses and manufacturers increasingly seek to comply with stricter environmental regulations.
Integration of Smart Technologies in Refrigeration Systems
Another emerging trend in the refrigerant market is the integration of smart technologies in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. The demand for energy-efficient and sustainable cooling solutions has accelerated the adoption of IoT (Internet of Things)-enabled systems that can monitor and optimize refrigerant use. Smart systems are equipped with sensors that track refrigerant levels, temperature, and system performance, enabling predictive maintenance, reducing energy consumption, and extending the lifespan of refrigeration units. Smart cooling systems are also contributing to cost savings, as they provide real-time data for better decision-making and the ability to perform maintenance before major breakdowns occur.
Expansion of HVAC Industry
The global refrigerant market is benefiting from the growing expansion of the HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) industry. This growth is fueled by increasing urbanization, rising living standards, and extreme weather conditions, which are driving the demand for residential and commercial air conditioning systems. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the number of air conditioners worldwide is projected to increase from 2.8 billion in 2021 to over 5.6 billion by 2050, with China, India, and other emerging markets seeing significant adoption. As the demand for air conditioning rises, the need for refrigerants is expected to grow. Also, manufacturers are aligning with regulatory standards by adopting lower-GWP refrigerants to meet sustainability goals. This trend is contributing to a surge in demand for traditional and next-generation refrigerants in the coming years.
Refrigerant Market Segment Insights
Refrigerant Market Outlook – by Type-Based Insights
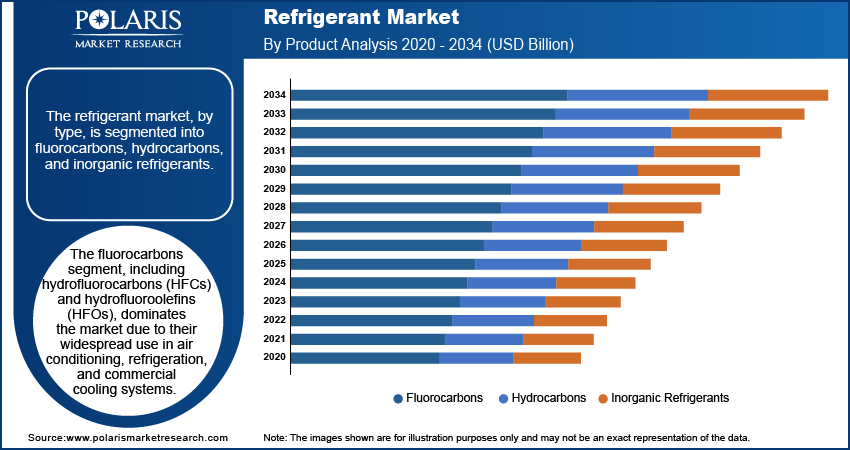
The refrigerant market, by type, is segmented into fluorocarbons, hydrocarbons, and inorganic refrigerants. The fluorocarbons segment, including hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs), dominates the market due to their widespread use in air conditioning, refrigeration, and commercial cooling systems. This segment is particularly favored for its efficiency and stability, although regulatory pressures surrounding environmental concerns are pushing for a gradual phase-out of high-GWP variants. In contrast, the hydrocarbons segment, encompassing refrigerants such as propane (R-290) and isobutane (R-600a), is witnessing significant growth. These refrigerants are gaining traction as low-GWP alternatives to fluorocarbons, offering improved energy efficiency and minimal environmental impact. As regulations tighten, hydrocarbons are increasingly becoming the preferred choice for residential and small-scale commercial systems.
Inorganic refrigerants, such as ammonia (R-717) and carbon dioxide (R-744), are also gaining prominence, particularly in industrial refrigeration systems due to their low environmental footprint and high efficiency in large-scale applications. Ammonia is especially favored in heavy industries such as food processing, while CO2 is increasingly utilized in commercial refrigeration due to its nontoxic and nonflammable properties. Among these, hydrocarbons are registering the highest growth, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable, energy-efficient cooling solutions. They are expected to capture a larger market share in the coming years. This growth is particularly evident in emerging markets where both regulatory frameworks and environmental awareness are pushing the adoption of alternative refrigerants.
Refrigerant Market Outlook – by Application-Based Insights
The refrigerant market, by application, is segmented into air conditioning, refrigeration, and others. The growing demand for air conditioning in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, particularly driven by rising temperatures and urbanization, is a major factor propelling the dominance of this segment. Air conditioning systems, particularly in regions such as North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific, are increasingly adopting refrigerants that comply with environmental regulations, such as low-GWP options, to reduce their carbon footprint. As a result, the air conditioning application remains a critical driver of refrigerant consumption, with significant growth observed in both developed and emerging markets.
The refrigeration segment is experiencing steady growth, with increasing demand for both commercial refrigeration systems and industrial applications, such as cold storage and food processing. This segment is gradually shifting toward more sustainable refrigerants, including natural refrigerants such as CO2 and ammonia, driven by stringent environmental standards. The others segment, which includes specialized applications such as heat pumps and refrigeration systems in the automotive industry, continues to grow at a slower rate. However, the air conditioning application is registering the highest growth, driven by technological advancements, climate change, and the expansion of HVAC systems globally.
Refrigerant Market Outlook – by End User-Based Insights
The refrigerant market, by end user, is segmented into industrial, commercial, and domestic. The Industrial segment, including food processing, chemical manufacturing, and large-scale refrigeration systems, demands significant volumes of refrigerants due to their energy-intensive operations and the need for specialized cooling solutions. This segment is also increasingly focused on adopting refrigerants with lower environmental impact, such as ammonia and carbon dioxide, due to stringent regulatory pressures and the need for more sustainable practices. The industrial end user category is crucial in driving the demand for refrigerants, as large refrigeration systems and cooling units in industries require high-efficiency refrigerants for optimal performance.
The commercial segment, encompassing sectors such as retail refrigeration, HVAC systems for office buildings, and refrigerated transport, is experiencing steady growth as businesses seek more energy-efficient and cost-effective cooling solutions. The rising demand for refrigeration in supermarkets, restaurants, and logistics, combined with the push for low-GWP refrigerants, is contributing to the growth of this segment. The domestic segment holds the smallest share, primarily driven by the increased adoption of air conditioning systems in households, particularly in emerging markets. However, it is the industrial segment that is registering the highest growth, supported by the expansion of manufacturing and logistics industries in key regions, particularly in Asia Pacific and North America.
Refrigerant Market Regional Insights
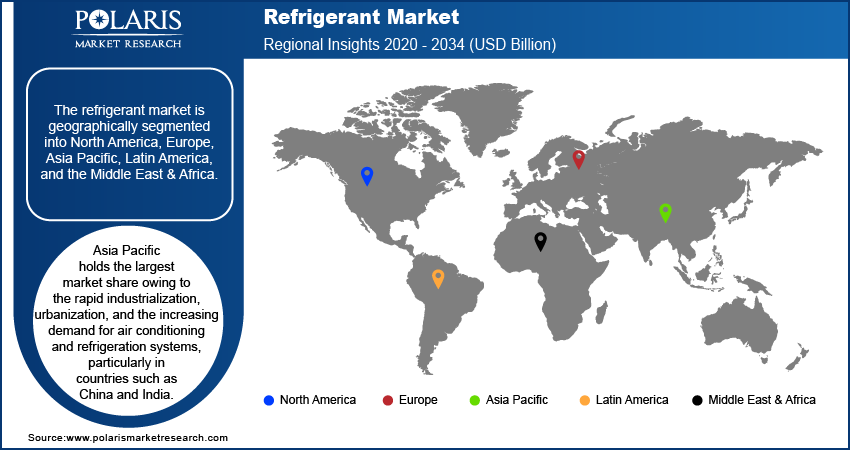
The refrigerant market is geographically segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. Asia Pacific holds the largest market share owing to the rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the increasing demand for air conditioning and refrigeration systems, particularly in countries such as China and India. The growing middle-class population, coupled with rising temperatures and the need for energy-efficient cooling solutions, fuels the demand for refrigerants in residential and commercial applications. Additionally, Asia Pacific is witnessing substantial investments in infrastructure development, boosting the demand for refrigeration in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and logistics. The region's market share is further supported by favorable government policies promoting the adoption of sustainable refrigerants and the ongoing transition to low-GWP alternatives.
Europe holds a significant share of the global refrigerant market, driven by strict environmental regulations and a strong focus on sustainability. The European Union’s F-gas regulation and the implementation of the Kigali Amendment have accelerated the transition toward low-GWP refrigerants such as HFOs, ammonia, and CO2. Industries in Europe, especially food processing, pharmaceutical, and HVAC, are increasingly adopting eco-friendly refrigerants to comply with stringent laws and reduce their carbon footprint. The region is also seeing growth in the adoption of smart refrigeration systems, with an increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions in commercial and industrial applications. As sustainability continues to be a priority, the refrigerant market in Europe is expected to witness steady growth, particularly with the rise in the use of natural refrigerants and ongoing regulatory support for climate action.
Refrigerant Market – Key Players and Competitive Insights
Chemours Company; Honeywell International Inc.; Arkema S.A.; Linde Group; Daikin Industries Ltd.; Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.; Dongyue Group Limited; Beijing Tongshi Chemical Co., Ltd.; Mexichem Fluor; Zhejiang Fluorsid Co., Ltd.; SINOCHEM International Corporation; The Dow Chemical Company; Koura (formerly known as Mexichem); Gujarat Fluorochemicals Ltd.; and Shanghai 3F New Materials Co., Ltd. are among the key players in the global refrigerant market. These companies are actively engaged in the production and distribution of refrigerants, with many focusing on developing and offering alternatives to traditional refrigerants that align with global environmental regulations. Notably, Chemours, a spin-off from DuPont, plays a key role in the market with its broad range of refrigerants, while Honeywell and Arkema focus on low-GWP solutions such as HFOs and HFCs. Daikin, along with Linde, is also heavily involved in the industrial-scale production of refrigerants and refrigeration equipment.
In terms of competition, companies are increasingly differentiating themselves based on their innovation and commitment to sustainability. Major players are investing heavily in research and development to produce refrigerants with lower environmental impact. This has become essential as regulations tighten, and companies aim to capture market share by offering solutions that meet the growing demand for energy-efficient and eco-friendly refrigerants. For instance, Dow and Honeywell are actively pushing forward with products that comply with new environmental standards, while others, such as Daikin and Linde, are integrating advanced refrigeration technologies to improve overall efficiency.
The competitive dynamics in the refrigerant market are influenced by regulatory pressures, technological advancements, and strategic collaborations. Companies are looking to expand their market presence not just through product innovation, but by securing long-term contracts and forging partnerships across various end-user industries such as HVAC, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. Additionally, as emerging markets continue to experience rapid growth in demand for air conditioning and refrigeration, players are strategically positioning themselves in regions such as Asia Pacific, where there is significant potential for expansion. The shift in adoption toward natural refrigerants and the development of alternatives to ozone-depleting substances further intensifies the competition, pushing companies to adapt and align with the global trend toward environmental sustainability.
Chemours is a global player in the refrigerant market, known for its production of a variety of chemicals, including refrigerants. The company focuses on providing solutions that meet environmental standards, with a significant portion of its portfolio aimed at replacing high-GWP refrigerants with more sustainable alternatives. Chemours has a strong presence in multiple regions and serves industries such as automotive, refrigeration, and air conditioning.
Honeywell is another key player in the refrigerant market, with a broad portfolio that includes a variety of refrigerants designed for industrial and commercial cooling systems. The company emphasizes providing solutions that help reduce energy consumption and environmental impact. Honeywell has been involved in advancing refrigerant technologies that comply with global regulations, including those aimed at reducing the use of high-GWP substances.
Key Companies in Refrigerant Market
- Chemours Company
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Arkema S.A.
- Linde Group
- Daikin Industries Ltd.
- Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.
- Dongyue Group Limited
- Beijing Tongshi Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Mexichem Fluor
- Zhejiang Fluorsid Co., Ltd.
- SINOCHEM International Corporation
- The Dow Chemical Company
- Koura (formerly Mexichem)
- Gujarat Fluorochemicals Ltd.
- Shanghai 3F New Materials Co., Ltd.
Refrigerant Industry Developments
- In May 2024, Chemours announced a partnership with a major European company to supply low-GWP refrigerants for use in commercial refrigeration systems. This move aligns with the ongoing push for environmentally friendly refrigerants and demonstrates the company’s focus on expanding its product range in line with changing regulations.
- In April 2024, Honeywell introduced a new line of low-GWP refrigerants for the automotive sector, supporting efforts to make vehicle air conditioning systems more energy-efficient and environmentally sustainable. This launch is part of the company’s ongoing strategy to develop products that align with global environmental and regulatory standards.
Refrigerant Market Segmentation
By Type Outlook
- Fluorocarbons
- Hydrocarbons
- Inorganic Refrigerants
By Application Outlook
- Air Conditioning
- Refrigeration
- Others
By End User Outlook
- Industrial
- Commercial
- Domestic
By Regional Outlook
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Refrigerant Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2024 |
USD 14.90 billion |
|
Market Size Value in 2025 |
USD 15.56 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 23.22 billion |
|
CAGR |
4.5% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global refrigerant market value reached USD 14.90 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 23.22 billion by 2034
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 4.5% during 2025–2034.
North America held the largest share of the global market in 2024.
A few key players in the global refrigerant market are Chemours Company; Honeywell International Inc.; Arkema S.A.; Linde Group; Daikin Industries Ltd.; Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.; Dongyue Group Limited; Beijing Tongshi Chemical Co., Ltd.; Mexichem Fluor; Zhejiang Fluorsid Co., Ltd.; SINOCHEM International Corporation; The Dow Chemical Company; Koura (formerly known as Mexichem); Gujarat Fluorochemicals Ltd.; and Shanghai 3F New Materials Co., Ltd.
The fluorocarbons segment accounted for the largest share of the global market in 2024.
The air conditioning segment accounted for the largest share of the global market in 2024.
A refrigerant is a substance or mixture used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems to absorb and release heat. It circulates within a closed-loop system, changing from a gas to a liquid and vice versa, to facilitate the cooling or heating process. Refrigerants are critical for applications such as home air conditioning, industrial cooling systems, and refrigeration for food preservation. They are chosen based on factors such as thermal efficiency, environmental impact, and compliance with regulatory standards, with a growing trend toward low-GWP (Global Warming Potential) and ozone-friendly options to reduce environmental harm.
A few key trends in the refrigerant market are described below: Shift Toward Low-GWP Refrigerants: Increasing adoption of refrigerants with lower global warming potential (GWP) due to stringent environmental regulations such as the Kigali Amendment. Regulatory Pressure: Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to phase out high-GWP refrigerants, driving the demand for alternative refrigerants. Rising Demand for Energy-Efficient Solutions: Increased focus on energy-efficient refrigerants that help reduce operational costs and meet sustainability goals in commercial and residential sectors. Growth in Emerging Markets: Rapid urbanization and industrialization in regions such as Asia Pacific are boosting demand for refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
A new company entering the refrigerant market must focus on sustainability and compliance with evolving environmental regulations to gain a competitive edge. Developing and offering low-GWP and natural refrigerants could attract environmentally conscious customers and ensure regulatory compliance. Additionally, investing in energy-efficient solutions and innovative technologies, such as smart refrigeration systems, would position the company as a leader in reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Companies producing and utilizing refrigerants and related products and other consulting firms must buy the report.
