
Global Rare Disease Diagnostics Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report, By Disease Type; By Product Type; By Sample Type; By Technology; By Test; By Age Group; By Trait Type; By End-User; By Region; Segment Forecast, 2024 - 2032
- Published Date:May-2024
- Pages: 118
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM4902
- Base Year: 2023
- Historical Data: 2019-2022
Report Outlook
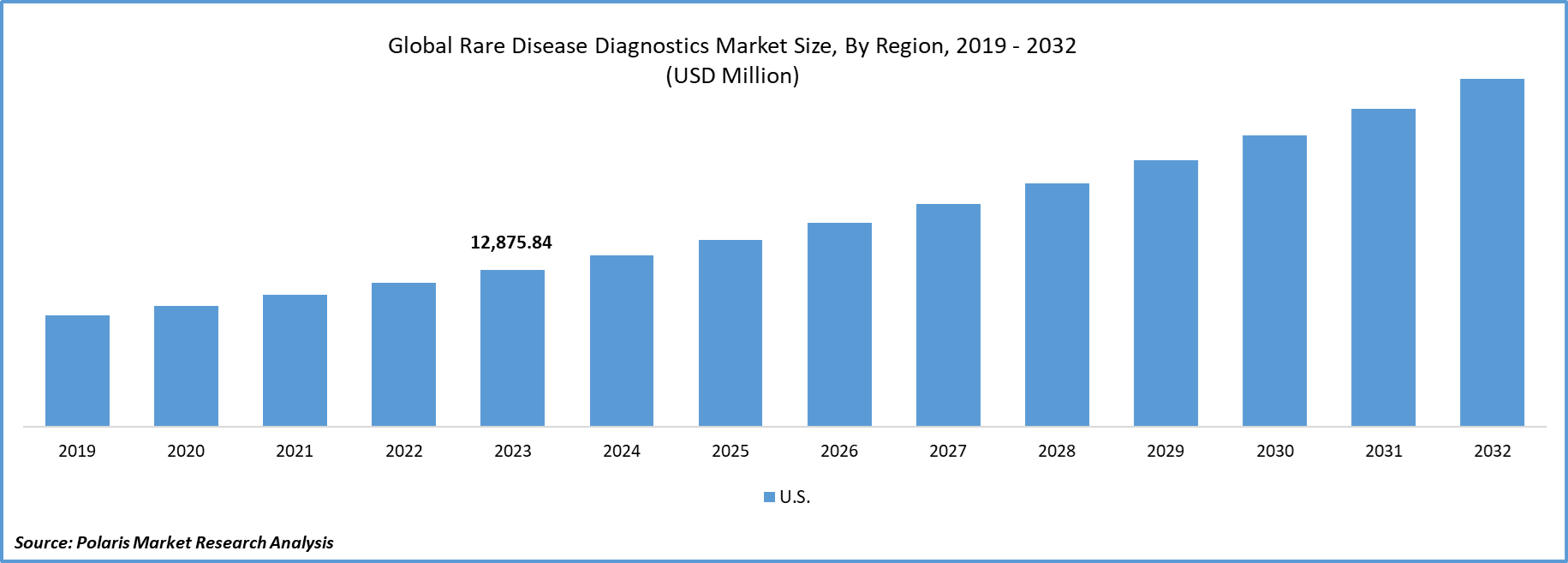
Global Rare Disease Diagnostics Market size was valued at USD 40,227.42 million in 2023. The market is anticipated to grow from USD 43,872.03 million in 2024 to USD 88,969.27 million by 2032, exhibiting the CAGR of 9.2% during the forecast period
Global Rare Disease Diagnostics Market Overview
Rare disease diagnosis represents a pivotal aspect of healthcare, focusing on identifying and managing medical conditions that affect a small percentage of the population. Rare diseases, also known as orphan diseases, typically afflict fewer than 1 in 2,000 individuals, varying in prevalence and severity. Despite their individual rarity, collectively, rare diseases impact millions worldwide, presenting significant challenges in diagnosis and treatment. These conditions often involve complex genetic, biochemical, or environmental factors, necessitating specialized diagnostic approaches and multidisciplinary care.
Rare diseases encompass a broad spectrum of disorders spanning various organ systems and medical specialties. Examples include genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis, a progressive lung disease caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy, a degenerative muscle disorder resulting from mutations in the DMD gene.
To Understand More About this Research:Request a Free Sample Report
Additionally, rare autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a chronic inflammatory condition affecting multiple organs, and rare cancers like mesothelioma, a tumor arising from the mesothelial cells lining the lungs or abdomen, fall under this category. Treatment for rare diseases varies depending on the underlying cause, disease progression, and individual patient factors. In some cases, symptomatic management and supportive care are the primary strategies aiming to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
For example, patients with cystic fibrosis undergo airway clearance techniques, receive nutritional support, and use medications to manage lung function and infections. In contrast, targeted therapies tailored to specific genetic mutations or disease pathways offer promising options for certain rare diseases. For instance, individuals with Duchenne muscular dystrophy benefit from exon-skipping drugs like eteplirsen, designed to restore dystrophin production and slow disease progression.
Moreover, advancements in gene therapy, stem cell transplantation, and precision medicine hold the potential to revolutionize the treatment landscape for rare diseases and offer hope to patients and their families.
Global Rare Disease Diagnostics Market Dynamics
Market Drivers
- Advances in genomic technologies drive diagnostic innovation.
Advances in genomic technologies have propelled diagnostic innovation for rare disease diagnosis, revolutionizing the way these conditions are identified and managed. These technological advancements encompass a spectrum of techniques, including Whole Exome Sequencing (WES), Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS), and advanced bioinformatics tools, which have significantly enhanced the precision and efficiency of genetic testing. As the cost of sequencing continues to decline and the speed of analysis improves, genomic testing has become more widely available, enabling healthcare providers to offer comprehensive genetic evaluations to patients with suspected rare diseases.
- Increasing awareness leads to higher demand for diagnostics
The heightened awareness surrounding rare diseases has sparked a surge in demand for diagnostic services aimed at identifying these conditions. As knowledge about rare diseases spreads among healthcare professionals, patients, and the general public, there is a growing recognition of the importance of early diagnosis and intervention. Several factors contribute to this trend, shaping the landscape of rare disease diagnostics. Furthermore, support efforts by patient organizations and rare disease foundations play a pivotal role in raising awareness and driving demand for diagnostic services. By highlighting the importance of early detection and access to specialized care, they empower patients and caregivers to advocate for themselves and seek out appropriate diagnostic testing.
Market Restraints
- High costs are likely to hamper the growth of the market.
The high cost associated with rare disease diagnosis presents a significant barrier for patients and healthcare systems alike, contributing to challenges in access to timely and accurate care. For instance, as per the study published by the National Library of Medicine, 2021, the use of genetic testing in patients with chronic kidney diseases was limited by the high cost of DNA sequencing. According to the National Institute of Health, the cost of genetic testing can range from under USD 100 to more than USD 2,000, depending on the nature and complexity of the test. Several factors contribute to the elevated costs involved in diagnosing rare diseases, impairing the financial burden on individuals and families affected by these conditions.
Report Segmentation
The market is primarily segmented based on disease type, product type, sample type, technology, test, age group, trait type, end-user, and region.
|
By Disease Type |
By Product Type |
By Sample Type |
By Technology |
By Test |
By Age Group |
By Trait Type |
By End-Use |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To Understand the Scope of this Report:Speak to Analyst
Global Rare Disease Diagnostics Market Segmental Analysis
By Disease Type Analysis
- The hematology and oncology segment led the diagnostics market with substantial revenue share and is anticipated to grow with healthy CAGR over the forecast period largely attributed to Rare blood disorders are a group of uncommon conditions that affect the blood, including red or white blood cells or platelets. These disorders can make it difficult to transport oxygen and control diseases, and some can be life-threatening. Examples of rare blood disorders include hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and Castleman disease. As extra cells accumulate in the blood or bone marrow, these diseases progressively cause anemia, fatigue, infection, or bleeding.
Rare hematology and oncology diseases are complex and challenging due to their low incidence rates, limited research, and often asymptomatic nature. The diagnostic process for rare blood disorders and cancers is inherently similar to that of common ones, involving a comprehensive array of techniques commonly utilized in the examination of prevalent diseases.
By Product Type Analysis
- The kits and reagents segment accounted for the largest market share and is likely to retain its market position with healthy CAGR throughout the forecast period as they are instrumental in isolating novel disease-causing genes rapidly and effectively, contributing to the identification of new disease-associated genes and improving diagnostic accuracy. Moreover, these kits and reagents are part of comprehensive options for biochemical and genetic testing, including enzyme testing, biomarker testing, and genetic confirmation through full gene sequencing, all of which are crucial for accurate rare disease diagnosis. Additionally, specialized kits and reagents are indispensable tools for healthcare professionals and researchers. These kits enable the precise analysis of genetic, molecular, and biochemical markers associated with rare conditions.
By End-Use Analysis
- Research laboratories and Contract Research Organizations (CROs) have dominated the market due to advancing rare disease diagnostics, contributing to the understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of these often-overlooked conditions. These laboratories and CROs offer specialized expertise and infrastructure necessary for conducting comprehensive genetic analyses, including next-generation sequencing, bioinformatics, and molecular diagnostics.
- The Diagnostics laboratories are witnessing substantial growth in the rare disease diagnostics market. This expansion can be attributed to several driving factors. Advancements in genetic sequencing technologies have made testing more accessible, accurate, and cost-effective. This has led to increased demand for rare disease diagnostics services, particularly for rare diseases, where early detection is paramount for better management.
Global Rare Disease Diagnostics Market Regional Insights
The North America region dominated the global market with the largest market share
- The North America region dominated the global market with the largest market share and is expected to maintain its dominance over the anticipated period. The growth of the segment market can be largely attributed to a variety of factors, including their low prevalence, nonspecific symptoms, and lack of awareness among healthcare providers. It can take years of testing and misdiagnoses before a correct rare disease diagnosis is made, during which time a patient's health can deteriorate. The costs related to rare disease diagnosis and treatment are substantial but difficult to track precisely.
- The Asia Pacific region is expected to be the fastest-growing region, with a healthy CAGR during the projected period. This region faces significant challenges in addressing rare diseases due to its large and diverse population, and its high prevalence is attributed to the region's heterogeneous population, complex healthcare environments, lack of unified definitions, limited treatment options, and inadequate funding. To address these challenges, the Asia Pacific Alliance of Rare Disease Organisations (APARDO) was established in 2015 to promote collaboration, increase awareness, and explore equitable and affordable diagnosis and treatment options to improve health outcomes for people living with rare diseases.
Competitive Landscape
The Global rare disease diagnostics market is fragmented and is anticipated to witness competition as companies leverage their strong R&D capabilities, diverse product offerings, and global presence to maintain their market position and players striving to gain market share through continual advancements in technology, strategic collaborations with other companies and research institutions, and a commitment to innovation. To stay abreast of evolving industry needs and adhere to stringent quality standards, companies are actively investing in research and development.
Some of the major players operating in the global market include:
- 3billion, Inc.
- Agilent Technologies, Inc
- CENTOGENE N.V.
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- FDNA™ INC
- GeneDx, LLC
- Illumina, Inc.
- Invitae Corporation
- Novo Nordisk A/S
- Quest Diagnostics
Recent Developments
- In February 2024, At the Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine, scientists and clinicians are achieving significant advancements in the diagnosis and treatment of rare diseases through the utilization of custom-made RNA, the cellular messenger.
- In January 2024, Quest Diagnostics revealed a partnership with Ultima Genomics to utilize Ultima's advanced high-throughput next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology in oncology and various disease fields. The objective is to enhance the availability of NGS testing to enhance cost-effectiveness and patient results in domains like minimal residual disease (MRD) testing.
Report Coverage
The Global Rare Disease Diagnostics market report emphasizes on key regions across the globe to provide better understanding of the product to the users. Also, the report provides market insights into recent developments, trends and analyzes the technologies that are gaining traction around the globe. Furthermore, the report covers in-depth qualitative analysis pertaining to various paradigm shifts associated with the transformation of these solutions.
The report provides detailed analysis of the market while focusing on various key aspects such as competitive analysis, disease type, product type, sample type, technology, test, age group, trait type, end-user and their futuristic growth opportunities.
Global Rare Disease Diagnostics Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2024 |
USD 43,872.03 million |
|
Revenue forecast in 2032 |
USD 88,969.27 million |
|
CAGR |
9.2% from 2024 – 2032 |
|
Base year |
2023 |
|
Historical data |
2019 – 2022 |
|
Forecast period |
2024 – 2032 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2024 to 2032 |
|
Segments covered |
By Disease Type, By Product Type, By Sample Type, By Technology, By Test, By Age Group, By Trait Type, By End-User, By Region |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, region and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global rare disease diagnostics market size is expected to reach USD 88,969.27 million by 2032
Key players in the market are CENTOGENE N.V., F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., FDNA™ INC, GeneDx, LLC, Illumina, Inc
North America contribute notably towards the global Rare Disease Diagnostics Market
Global Rare Disease Diagnostics Market exhibiting the CAGR of 9.2% during the forecast period
The Rare Disease Diagnostics Market report covering key segments are disease type, product type, sample type, technology, test, age group, trait type, end-user, and region.
