
Power Grid Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Components (Cables, Variable Speed Drivers, Transformers, Switchgear, Others), By Power Source, By Application, By Region, Segments & Forecast, 2023 – 2032
- Published Date:Apr-2023
- Pages: 116
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM3137
- Base Year: 2022
- Historical Data: 2019-2021
Report Outlook
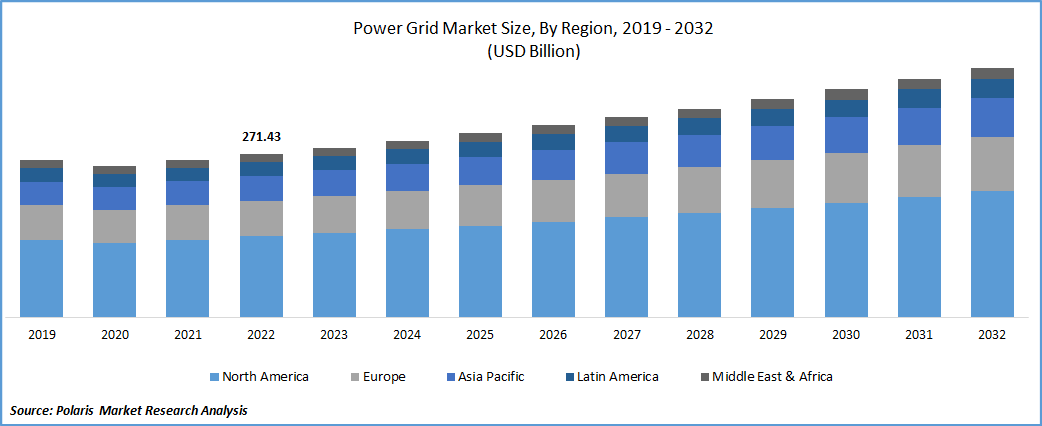
The global power grid market was valued at USD 271.43 Billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.37% in the forecast period. The growing energy need from residential and industrial sectors, the shift towards renewable energy sources, and the adoption of new technologies are the key factors projected to drive the market in the forecast period. There is a growing trend towards decentralized power generation, where smaller-scale power generation facilities, such as solar panels and wind turbines, are closer to end-users. This trend is driven by advances in renewable energy technologies and the desire to improve energy efficiency and reduce transmission and distribution losses.
Know more about this report: Request for sample pages
Power grids, also known as electric or electrical, are networks of power generation, transmission, and distribution facilities that provide electricity to homes, businesses, and other organizations. The power grid consists of three main components: power generation, transmission, and distribution. Power generation involves the production of electricity at power plants, which can use various energy sources, including fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower.
Power generation involves the production of electricity at power plants, which can use various energy sources, including fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower. The transmission component of the power grid involves the movement of electricity from power plants to distribution networks, typically through high-voltage transmission lines that can span hundreds of miles. The distribution component of the power grid involves the movement of electricity from the transmission network to homes, businesses, and other end-users.
For instance, as per International Energy Agency, the global electricity demand grew by over 6% (over 1,500 TWh) in 2021, the largest percentage growth since 2010. About half of the global growth is estimated to be contributed by China, and the Industrial sector is the largest contributor to the energy demand in the same period.
The higher installation cost of transmission systems and the lack of infrastructure are two important restricting factors in the market. The installation cost of transmission systems can be very high, particularly for long-distance transmission lines that must traverse difficult terrain or cross bodies of water. As new safety and environmental regulations are introduced, the cost of installing and maintaining transmission lines can also increase over time. The high price of transmission infrastructure can pose a significant barrier to developing power grids, particularly in areas with relatively low electricity demand.
In addition to the high cost of transmission infrastructure, the lack of infrastructure can be a significant restricting factor for the market. Many regions of the world lack the infrastructure required to support the development of power grids, particularly in rural or remote areas. It can make it difficult or impossible for utilities to connect these areas to the main power grid, leaving many people needing access to electricity.
Know more about this report: Request for sample pages
Industry Dynamics
Growth Drivers
Rapid urbanization and digitalization are two key driving factors in developing power grids in modern societies. Urbanization has led to a significant increase in the electricity demand as more people move into cities and require access to energy to power their homes and businesses. It pressures existing power grids to expand and modernize to meet the growing electricity demand. Additionally, urbanization has led to the emergence of new power generation technologies, such as rooftop solar panels and wind turbines, which are becoming increasingly popular among urban residents.
Digitalization is also playing an important role in the development of power grids. The increasing use of digital technologies, such as smart grids and advanced metering systems, is helping to improve the efficiency and reliability of power grids. For example, smart grids use advanced sensors and communication technologies to monitor and manage the flow of electricity, enabling utilities to detect and respond to disruptions more quickly and effectively.
Investments in upgrading and expanding transmission and distribution (T&D) infrastructure are other driving factors in the market. Investments in T&D infrastructure are also driven by the need to modernize the power grid and make it smarter. It involves the integration of advanced technologies such as sensors, automation systems, and data analytics tools to enable real-time monitoring and control of the grid. The adoption of smart grid technologies is expected to significantly improve the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of the power grid.
Report Segmentation
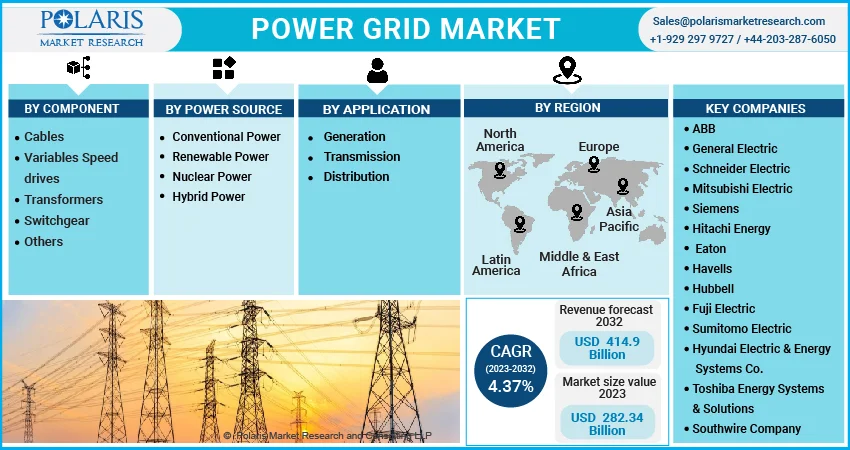
The market is primarily segmented based on component, power source, application, and region
|
By Component |
By Power Source |
By Application |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
Know more about this report: Request for sample pages
The Cables segment is anticipated to dominate the market in the forecast period.
The cable segment's growth is driven by several factors, including the increasing demand for electricity, the need to upgrade aging infrastructure, and the growing adoption of renewable energy sources. Cables are a critical component of the power grid, as they enable the transmission and distribution of electricity over long distances.
In addition, advancements in cable technologies, such as developing high-temperature superconducting cables, are expected to fuel growth in this segment further. The increasing demand for electricity, particularly in emerging economies, is driving the need for new and expanded transmission and distribution infrastructure, which in turn requires the installation of more cables.
Renewable Power is projected to witness the fastest CAGR in the forecast period.
The Renewable Power segment for market is experiencing significant growth due to several factors. One of the primary drivers of development is the increasing demand for clean and renewable energy sources, driven by concerns over climate change and environmental sustainability.
Governments worldwide are also promoting the growth of the Renewable Power segment in the market through policies such as renewable energy targets, feed-in tariffs, tax credits, and other incentives. It has led to significant investments in renewable power generation and transmission infrastructure, which is expected to continue in the coming years.
The Distribution segment is projected to constitute a major share in the forecast period.
The distribution segment of the power grid is responsible for the final delivery of electricity to end-users, including homes, businesses, and other institutions. The growth of the distribution segment is being driven by several factors, including the increasing demand for electricity, the need to modernize aging infrastructure, and the adoption of new technologies that enable more efficient and sustainable distribution of electricity.
Finally, adopting new technologies, such as distributed energy resources (DERs) and energy storage systems, also drives growth in the distribution segment. DERs, such as rooftop solar panels and small wind turbines, are becoming more common, and utilities are investing in technologies that enable more efficient integration of these resources into the distribution grid.
The transmission segment is anticipated to witness a significant growth rate. One of the primary drivers of growth in the transmission segment is the increasing electricity demand. As the electricity demand grows, new transmission infrastructure increases, including installing new transmission lines, transformers, and substations. Another factor driving growth in the transmission segment is integrating renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar Power, into the power grid.
Asia Pacific region is projected to witness the fastest CAGR in the forecast period.
Increasing electricity demand is one of the primary drivers of growth in the Asia Pacific power grid market. The population in the Asia Pacific region is growing, so the electricity demand is increasing. Utilities invest in new power generation capacity and transmission and distribution infrastructure to meet the demand.
Finally, the growing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar Power, drives growth in the Asia Pacific power grid market. Many countries in the region have implemented renewable energy targets and policies to promote the adoption of renewable energy sources. It has led to the construction of new renewable energy facilities, which require new transmission infrastructure to connect to the grid.
Competitive Insight
Some of the prominent key players operating in the Marketspace includes ABB, General Electric, Schneider Electric, Mitsubishi Electric, Siemens, Hitachi Energy, Eaton, Havells, Hubbell, Fuji Electric, Sumitomo Electric, Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems Co., Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions, Southwire Company.
Recent Developments
- June 2022: Hitachi Energy and Schneider Electric have entered a non-exclusive collaboration to offer enhanced customer value and quicken the energy transition. Schneider Electric has been able to use Hitachi’s high-voltage portfolio, while Hitachi can leverage Schneider’s medium-voltage portfolio.
- August 2021: Mitsubishi Electric Corporation has acquired UK-based Smarter Grid Solutions (SGS), a key provider of distributed energy sources software, to enhance power utilities in Europe and North American region and manages renewable energy sources.
Power Grid Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2023 |
USD 282.34 Billion |
|
Revenue forecast in 2032 |
USD 414.91 Billion |
|
CAGR |
4.37% from 2023 - 2032 |
|
Base year |
2022 |
|
Historical data |
2018 - 2021 |
|
Forecast period |
2023 - 2032 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD Billion and CAGR from 2023 to 2032 |
|
Segments covered |
By Component, By Power Source, By Application, By Region |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Key companies |
ABB, General Electric, Schneider Electric, Mitsubishi Electric, Siemens, Hitachi Energy, Eaton, Havells, Hubbell, Fuji Electric, Sumitomo Electric, Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems Co., Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions, Southwire Company |
FAQ's
Key companies in power grid market are ABB, General Electric, Schneider Electric, Mitsubishi Electric, Siemens, Hitachi Energy, Eaton, Havells, Hubbell, Fuji Electric, Sumitomo Electric, Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems Co.
The global power grid market expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.37% in the forecast period.
The power grid market report covering key segments are component, power source, application, and region.
Key driving factors in power grid market are electrification of industrial processes and fleets.
The global power grid market size is expected to reach USD 414.91 Billion by 2032.
