
Periodic Fever Syndrome Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report, By Indication (Hyperimmuno-globulinemia D Syndrome (HIDS), Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF), TNF Receptor-Associated Periodic Syndrome (TRAPS), Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndrome (CAPS) Others); By Treatment; By End-Use; By Region; Segment Forecast, 2024 - 2032
- Published Date:Dec-2023
- Pages: 119
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM4152
- Base Year: 2023
- Historical Data: 2019-2022
Report Outlook
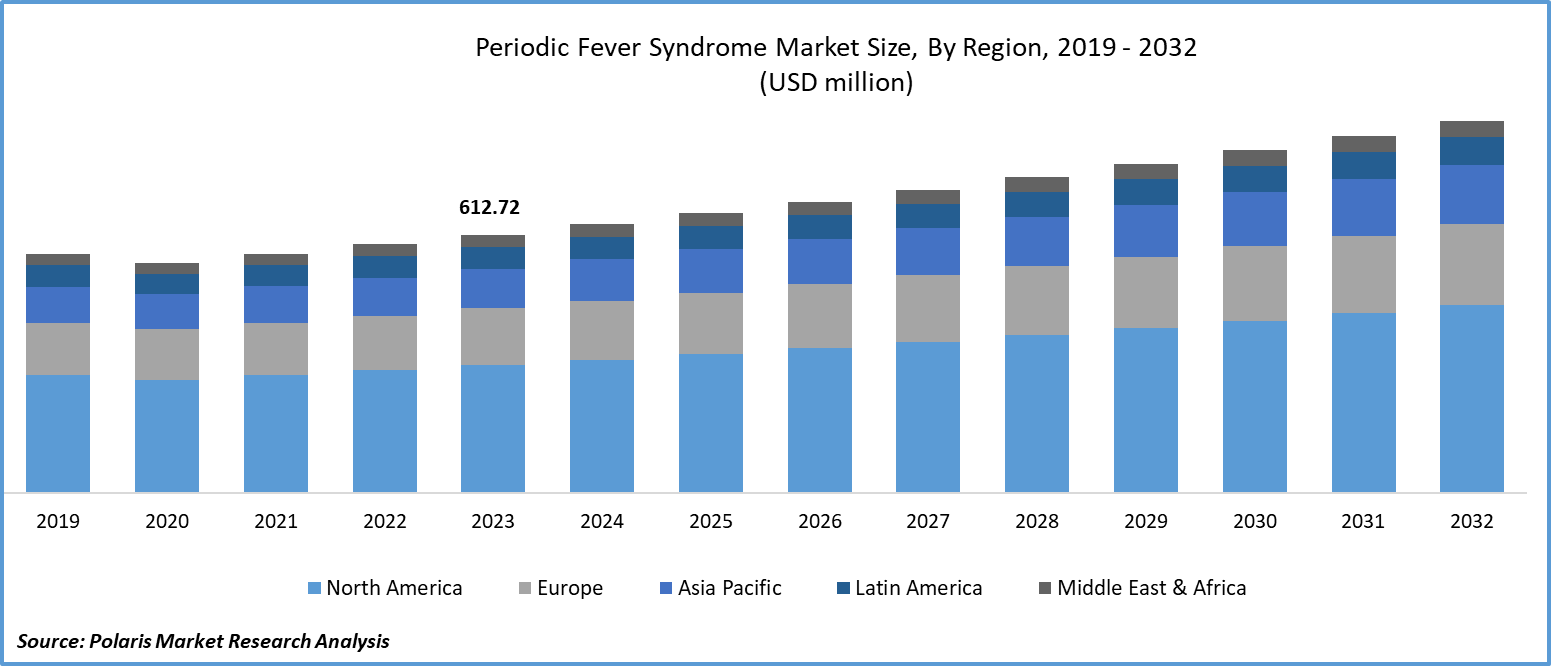
The global periodic fever syndrome market was valued at USD 612.72 million in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.1% during the forecast period.
Periodic Fever Syndrome (PFS) is an autoinflammatory condition that causes recurrent sickness. It is not caused by an infectious agent. Periodic Fever Syndrome is a hereditary disorder that can manifest itself in childhood. Genetic tests and clinical characteristics are used to determine it. The patient's afflicted region, age, and location are all crucial considerations. Understanding genetic abnormality is essential for therapy. Although the symptoms of recurrent fever syndrome are similar, the patterns of heredity, etiology, and frequency of bouts vary.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Many organs and tissues can be affected by Periodic Fever Syndrome. During assaults, it also has high temperatures. Elevated blood levels of acute phase reactants such as fibrinogen, serum amyloid A, and leukocytosis are related to periodic fever syndrome. Periodic Fever Syndrome affects various organs and tissues and has its own set of symptoms in addition to high fever during episodes. Periodic fever syndrome is linked with elevated blood levels of acute-phase reactants such as fibrinogen and serum amyloid A, leukocytosis, and a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
An aspect influencing market expansion is increased healthcare spending. The market will expand as a result of technical developments, increasing public and private awareness efforts, and more government financing. The periodic fever market will also be influenced by increased demand for efficient therapies and an aging population. The market will also expand as a result of strong disposable income and a preference for a sedentary lifestyle. The periodic fever market will also benefit from increased R&D activity and the introduction of new effective medicines. Because of unmet medical demands and developments in healthcare technology, the market will increase at a quicker rate.
For Specific Research Requirements, Request for a Customized Research Report
Industry Dynamics
Growth Drivers
- Growing awareness among healthcare professionals, patients
Currently, oral anti-inflammatory medicines such as corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), among others, are used to treat periodic fever syndrome, which helps to control the disease's symptoms but does not aid in its eradication. However, significant technical improvements and increased research activity are resulting in the creation of enhanced diagnostic facilities as well as novel medications and cures. The new pharmacological approvals for the treatment of this uncommon condition are likely to boost the growth of the periodic fever syndrome business.
Furthermore, the increase in R&D efforts and the launch of innovative medicines would create positive prospects for the periodic fever syndrome market. In addition, the high unmet demand for current therapy and advancements in healthcare technology will drive the growth rate of the periodic fever syndromes market in the future.
Report Segmentation
The market is primarily segmented based on indication, treatment, end-use, and region.
|
By Indication |
By Treatment |
By End-Use |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
To Understand the Scope of this Report: Speak to Analyst
By Indication Analysis
Hyperimmuno Globulinemia D syndrome (HIDS)is predicted to dominate the industry's market segment. The genetic condition Hyperimmuno globulinemia D Syndrome (HIDS) is characterized by recurring fevers, arthritis, and a rash. Some people with HIDS may develop amyloidosis, a condition in which aberrant proteins collect in certain organs such as the liver or kidneys, causing organ damage hence it is likely to augment the periodic fever syndrome market.
Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is the most prevalent hereditary autoinflammatory illness, affecting approximately one in every 200 persons of Arab-Jewish heritage in the Near East. It also appears to be prevalent in all people descended from this region, including Asians and Hispanics. The illness often presents throughout childhood, with fever bouts lasting an average of five days but continuing up to three weeks or longer without treatment. The reappearance of the disease is frequently brought on by a viral illness or by medicines such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) resulting in widely accelerating the market growth.
TNF Receptor-Associated Recurrent Syndrome is a rare disorder in which the immune system produces an antibody known as an anti-interleukin-l converting enzyme (anti-ICE), which causes inflammation and periodic fever. It most commonly affects young children and teens, although it can also impact adults. It happens when the body's immune system produces an antibody that assaults and kills a specific enzyme known as an interleukin-l converting enzyme (ICE). This enzyme aids in the regulation of inflammation in the body. This condition impairs proper infection-fighting and blood clotting because there is relatively little IgM.
By Treatment Analysis
NSAIDs inhibit the formation of certain substances in the body that cause inflammation. NSAIDs are effective in the treatment of pain produced by gradual tissue deterioration, such as arthritic discomfort. NSAIDs are also effective in treating back pain, menstrual cramps, and headaches. NSAIDs function similarly to corticosteroids (commonly known as steroids), but without many of the negative effects associated with steroids. Steroids are synthetic medications that mimic cortisol, a naturally occurring hormone. NSAIDs, decrease the pain & inflammation that typically accompany joint and muscle disorders & accidents.
Fever is treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), but musculoskeletal and stomach discomfort do not respond to NSAIDs and must be treated with corticosteroids; none of these treatments can prevent episodes. Etanercept is an anti-TNF medication that reduces the severity, length, and frequency of attacks. Treatment with anakinra, an IL-1 inhibitor, may potentially be beneficial. Infliximab, an anti-TNF antibody, should not be administered since it might cause paradoxical inflammatory responses.
Anti-interleukin-1 (IL-1) therapy (anakinra or canakinumab) has been shown to be beneficial in severe instances that have not responded to prior therapies. Etanercept has been demonstrated to be a successful treatment in certain people and can be used when other treatments are ineffective or have undesirable side effects. Tocilizumab (Actemra), a drug that blocks interleukin-6, has also proved useful in rare circumstances. Canakinumab was recently approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat this illness.
Recent research suggests that statins may be useful in various inflammatory disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis. Simvastatin has been demonstrated to lessen inflammation in hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome.
By End-Use Analysis
In hospitals, periodic fever syndrome can be employed for specific medical operations such as bone marrow transplantation and stem cell transplantation. Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D Syndrome is particularly efficient in lowering the risk of infection during these hospital processes when microorganisms are more likely to be present.
The practice of drug management in a retail context is known as retail pharmacy. This involves giving patients prescriptions and other services, which is usually done in an independent or chain pharmacy. Online pharmacies are also included in this category if they sell prescription pharmaceuticals as well as over-the-counter treatments that do not require a prescription.
Regional Insights
North America is a market leader in the worldwide periodic fever syndrome sector. Because of the expanding penetration of the region's key companies and the increased emphasis on patient care and monitoring, the region accounts for a large portion of the total market value. Growing investments in R&D activities, along with the availability of superior healthcare infrastructure in the area, are assisting industry expansion in North America. However, the difficulty in diagnosing periodic fever syndrome due to unrelated symptoms remains a major barrier for market participants.
Europe's Periodic Fever Syndrome market share is predicted to rise rapidly in the coming years. During the projection period, the expanding elderly population and an increase in the number of people diagnosed with periodic fever syndrome will boost development possibilities for the European market. Asia Pacific developing nations are seeing rapid expansion in the healthcare business. More elderly population, increased disposable income, and technological improvement would enhance demand for Periodic Fever Syndrome Drugs. India is predicted to be the fastest-growing market due to a growth in the incidence rate of Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D Syndrome, which has significantly contributed to the sales of period fever syndrome medications in recent years.
Key Players & Competitive Insight
Some of the major players operating in the global market include
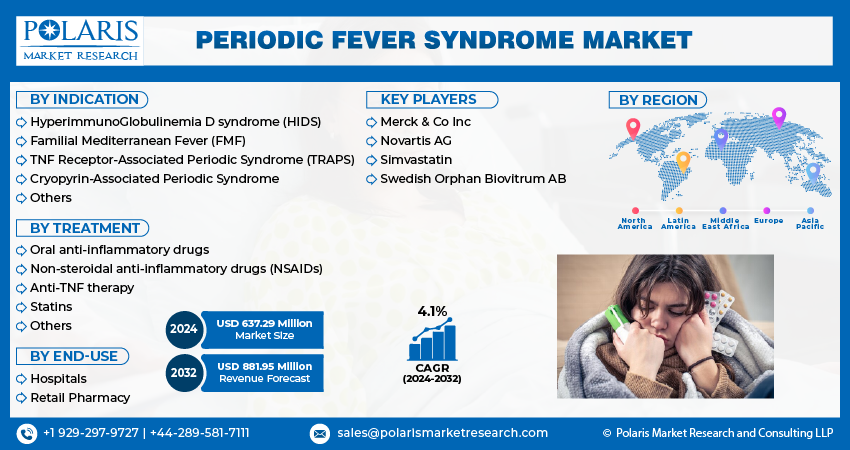
- Merck & Co Inc
- Novartis AG
- Simvastatin
- Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB
Recent Developments
- The National Human Genome Research Institute's researchers have identified clues to the origins of non-contagious, reoccurring fevers and sores in youngsters. Several genes have been linked to periodic fever syndrome, potentially leading to the development of novel therapies. Because of the nature of recurrent fever syndrome, experts have long suspected that the answer may be found in genomics.
Periodic Fever Syndrome Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2024 |
USD 637.29 million |
|
Revenue forecast in 2032 |
USD 881.95 million |
|
CAGR |
4.1% from 2024 - 2032 |
|
Base year |
2023 |
|
Historical data |
2019 - 2022 |
|
Forecast period |
2024 – 2032 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2024 to 2032 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Indication, By Treatment, By End-Use, By Region |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, region, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
key companies in periodic fever syndrome market are Merck & Co Inc, Simvastatin, Swedish Orphan Biovitrum AB
The global periodic fever syndrome market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4.1% during the forecast period.
The periodic fever syndrome market report covering key segments are indication, treatment, end-use, and region.
key driving factors in periodic fever syndrome market are growing awareness among healthcare professionals, patients
The global periodic fever syndrome market size is expected to reach USD 881.95 million by 2032
