
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Drug Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report, By Product (Off-Label Drugs, Budesonide Oral Suspension, Fluticasone ODT, Mepolizumab, Reslizumab, Benralizumab, Dupilunab, Omalizumab, QAX576, AKOO2, and Losartan); By Diagnosis; By Treatment; By Regions; Segment Forecast, 2021 - 2028
- Published Date:Jan-2021
- Pages: 111
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM1792
- Base Year: 2020
- Historical Data: 2016 - 2019
Report Outlook
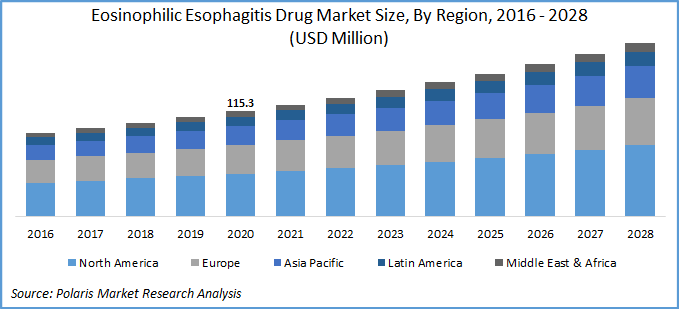
The global eosinophilic esophagitis drug market was valued at USD 115.3 million in 2020 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period. Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) is an antigen mediated chronic esophageal disease characterized clinically by esophageal dysfunction and histologically characterized by inflammation of the esophagus with eosinophils.
Eosinophilic esophagitis development is due to the presence of a deficient mucosal barrier in the esophagus and reverse immune reaction causing fissures/lesions, fibrosis, and dysmotility in the esophagus, mediated by Th2 interleukins. Eosinophilic esophagitis is multi-factorial, with around a 7 percent risk of genetic inheritance. Food allergies, and exposure to excessive use of antibiotics, acid suppression, and early life symptoms of gastro-intestinal disorders are also predominant market factors.
If left untreated, eosinophilic esophagitis could lead to a stricture in the esophagus, possible risks of food impaction, and dysphagia. As per the study conducted by Dellon and Hirano, in 2017, eosinophilic esophagitis has an annual incidence of 5 to 10 cases per 100,000 individuals and a prevalence of around 50 - 100 cases per 100,000 individuals. Clinical symptoms vary with age and sex, being predominant in males as compared to females. Infants with eosinophilic esophagitis face feeding difficulties, school kids suffer from vomiting and pain while eating, and adults show food impaction and dysphagia.
Despite pathologic advances in eosinophilic esophagitis, still there is no single FDA-approved drug for EoE. Currently, EoE is being treated with off-label treatments using 3 Ds: topical corticosteroids, dietary restrictions, and endoscopic dilation. Though in the past decade, few new eosinophilic esophagitis treatments were evolved such as steroid formulations optimizing mucosal deposition, with the recent approval of budesonide effervescent tablet in the European market, biologics used in the TH2-mediated diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, asthma, and other allergic reaction, currently being in clinical trials, and novel dietary restrictions.
Know more about this report: request for sample pages
Industry Dynamics
Growth Drivers
Recently, the potential drug candidates for the treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis have received promising results, which is expected to drive the market forward. In September 2020, Sanofi’s drug candidate Dupixent (dupilumab) received breakthrough therapy designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat eosinophilic esophagitis patients of 12 years and older in collaboration with Regeneron.
Dupixent is the fully human monoclonal antibody that inhibits the signaling of interleukin 4 and 5 proteins, regarded as primary instigators in type 2 inflammations, including EoE. This designation was based on the positive results of part A of phase 3 trials in patients suffering from EoE. Currently, there are no FDA-approved drugs for eosinophilic esophagitis, a progressive type 2 inflammatory disease damaging the functioning of the esophagus.
In the U.S. alone, there are around 160,000 people suffering from eosinophilic esophagitis and are treated with un-approved off label drugs and diet modifications. Among these, around 50,000 have repeated course of treatment. Part A of the phase 3 trial was the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which 81 patients met both primary and secondary endpoint. Enrolled patients were administered with a weekly dose of Dupixent 300 mg over a treatment period of 24-weeks. Patients examined had a reduction in primary symptoms, esophagus inflammation, and reduced eosinophil count on the esophagus mucosal membrane.
Moreover, in August 2019, AstraZeneca announced that FDA has granted orphan drug designation to its drug candidate Fasenra (benralizumab), used in the treatment of EoE. FDA grants this status to drug candidates which are intended to prevent rare disorders/diseases, affecting less than 200,000 individuals in the U.S. market. Drug depletes eosinophils present in both blood and connective tissue during eosinophilic esophagitis treatment and is undergoing clinical trials to test its specificity and efficacy. Currently, there are no FDA-approved drugs for eosinophilic esophagitis treatment, so there is a race among market players to have a first-mover advantage.

Know more about this report: request for sample pages
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Drug Market Report Scope
The market has been segmented on the basis of product, diagnosis, treatment, and region:
|
By Product |
By Diagnosis |
By Treatment |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
Know more about this report: request for sample pages
Insight by Product
Based on the product, the eosinophilic esophagitis drug market is categorized into off-label drugs, budesonide oral suspension, fluticasone ODT, Mepolizumab, Reslizumab, Benralizumab, Dupilunab, Omalizumab, QAX576, AKOO2, and Losartan. In 2020, the Dupilunab market segment accounted for the largest revenue share. Dupixent is the fully human monoclonal antibody that inhibits the signaling of interleukin 4 and 5 proteins, regarded as primary instigators in type 2 inflammations, including EoE. This designation was based on the positive results of part A of phase 3 trials in patients suffering from eosinophilic esophagitis.
Insight by Treatment
Based on the treatment, the global eosinophilic esophagitis drug market is bifurcated into dietary therapy, medication, dilation, others. In 2020, the dietary therapy market segment accounted for the largest share, among all. This high market segment share is due to unmet needs, for instance, the natural history of food sensitization and associated reactions in eosinophilic esophagitis patients, is still not clear. Study shows that less than 10 percent of kids regain their ability to have all kinds of food, previously being eliminated from their routine diet. However, clinical characteristics that align with food being introduced remain elusive and there are not any predictive indexes for its success or failure.
Moreover, current allergy testing for the food triggers in eosinophilic esophagitis has variable results, depending on test type and food being tested. In kids, the combined patch-based diets and skin prick have a moderate success rate of 50-60 percent, however, in adults, these tests show a very low success ratio to predict allergic food triggers. Many questions still to be ascertained in EoE, including a proof for antigen-specific T cells, and the timing of immunologic shift during food reaction from innate to adaptive immunity. Such questions in combination with the impact of food triggers in EoE drives the need for new allergy testing tests for EoE.
Geographic Overview
Geographically, the market is segregated as North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, South America, and Middle East & Africa. North America market is the largest regional revenue contributor followed by Europe and the Asia Pacific market. The competition among market players to have first-mover advantage, as there is no FDA approved drug for EoE and rising economic burden. In the U.S. alone, around 160,000 people are suffering from eosinophilic esophagitis and are treated with un-approved off label drugs and diet modifications. The annual healthcare burden of EoE in the U.S. alone costs about USD 1.4 billion.
Several dedicated associations and academic institutions such as Rare Diseases Clinical Research Network (CEGIR) and the American Partnership for Eosinophilic Disorders (APFED), particularly in developed economies are responsible for providing research grants and funding. For instance, in 2020, the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI) and APFED awarded a grant of USD 140,000 for two years to study how the immune system interacts with food allergy substances causing the onset of EoE in patients. The research will also contribute to identifying new targets for drug development and disease pathogenesis.
Moreover, Joshua B. Wechsler, the assistant professor at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine received a research grant of USD 100,000 for 2020-21, for its project to understand the role of mast cells in eosinophilic esophagitis, endoscopic abnormalities, and the impact of possible treatment. The project would analyze novel pathways from biopsies and understand the interactions of mast cells and associated mediators.
Competitive Insights
The prominent market players operating are Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Adare Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Takeda (Shire), DBV Technologies, Dr. Falk Pharma GmbH, Allakos, Inc., Arena Pharmaceuticals, and Ception Therapeutics.
In September 2020, the U.S.-based private equity firm TPG Capital announced the establishment of a new firm “Ellodi Pharmaceuticals” in the market. The new company will be dedicated to the clinical development of APT-1011, a novel candidate for the treatment of EoE, spun out from Adare Pharmaceuticals. APT-1011 is currently into phase 3 (FLUTE II) study.
