
Blue Ammonia Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report, By Technology (AutoThermal Reforming (ATR), Haber-Bosch Process); By Manufacturing Process; By Distribution Channel; By Application; By End-Use; By Region; Segment Forecast, 2024 - 2032
- Published Date:Jan-2024
- Pages: 118
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM4024
- Base Year: 2023
- Historical Data: 2019-2022
Report Outlook
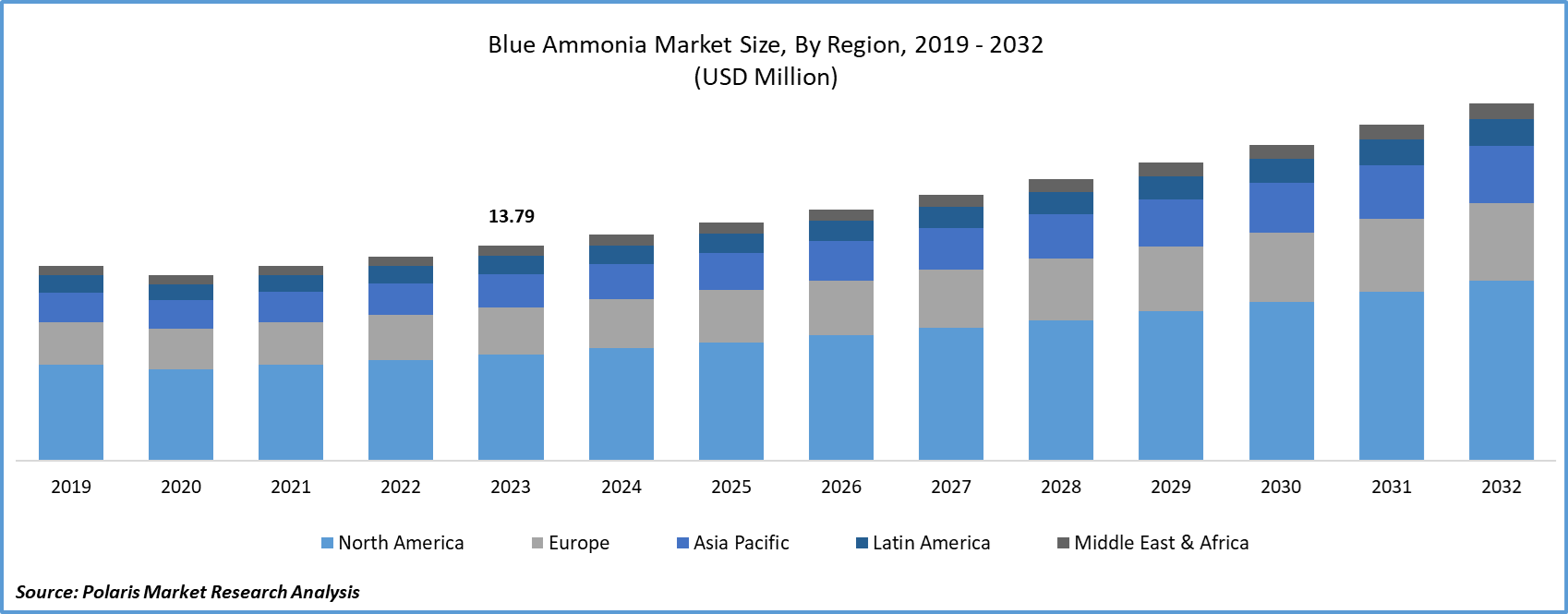
The global blue ammonia market was valued at USD 13.79 million in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.90% during the forecast period.
The increasing demand for low-carbon fuels across various industries is propelling the growth of market revenues. Growing concerns about climate change and the imperative to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have generated a substantial global need for low-carbon fuels. Blue ammonia, a potential low-carbon fuel, finds applications in diverse sectors such as fertilizer production, electricity generation, and transportation.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Blue low-carbon ammonia, when integrated with carbon capture technology, can effectively reduce its carbon emissions by over 90%. Industries and nations committed to achieving net-zero emissions are increasingly turning to blue ammonia due to its promising potential as a long-term energy source and a means of significantly lowering greenhouse gas emissions, ultimately transforming it into a low- or zero-carbon fuel.
As an example, Japan is actively exploring the adoption of ammonia, with the goal of eventually transitioning to it as its primary energy source. They are currently conducting tests on co-firing ammonia alongside coal in their power plants to minimize carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. This co-firing approach involves the use of ammonia, a chemical composed of nitrogen and hydrogen, in their coal-powered facilities. Japan has also reached out to other G7 countries to garner support for this initiative.
The market's revenue growth is being propelled by the potential of blue ammonia as a fuel for both transportation and power generation. Ammonia is increasingly finding application in turbine engines, either through direct combustion or as an indirect source for industrial processes by converting it back into nitrogen and hydrogen. Notably, ammonia boasts several advantages over liquid hydrogen, making it a more practical choice. Unlike liquid hydrogen, ammonia doesn't necessitate cooling to extremely low temperatures and offers a higher energy density.
Conversely, the challenges associated with hydrogen, including high storage costs, purity requirements, and transportation complexities, underscore the advantages of ammonia. These benefits suggest that ammonia could serve as a viable option for decarbonizing energy-intensive sectors, particularly in power generation and transportation. This is a significant driver of market revenue growth.

Furthermore, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, where Russia is a major fertilizer exporter, has created a surge in demand for ammonia production. Export restrictions are now compelling countries to seek alternative supply sources. Nations that previously relied on fertilizer imports but now require local supply sources are contributing to the increased demand for additional fertilizer production. This, in turn, fuels the demand for blue ammonia.
Industry Dynamics
Growth Drivers
- Growing initiatives aimed at bolstering the hydrogen-based economy.
The utilization of hydrogen gas as a primary energy source in power generation, transportation, and industrial processes plays a pivotal role in the shift towards a hydrogen-based economy. The imperative drives this transition to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, decrease dependence on fossil fuels, and combat climate change challenges. Blue ammonia emerges as an intriguing fuel option in the journey toward a hydrogen economy due to its low carbon emissions and versatile applications. Blue ammonia is gaining momentum as a promising clean energy carrier and fuel source. It is generated by capturing carbon dioxide emissions from industrial activities and utilizing them in the synthesis of ammonia, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional ammonia production methods.
Report Segmentation
The market is primarily segmented based on technology, manufacturing process, distribution channel, application, end-use, and region.
|
By Technology |
By Manufacturing Process |
By Distribution Channel |
By Application |
By End-Use |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
|
|
To Understand the Scope of this Report: Speak to Analyst
By Manufacturing Process Analysis
- The Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) segment held the largest revenue share in 2022
The Steam Methane Reforming (SMR) category is projected to dominate the global blue ammonia market in terms of revenue share during the forecast period. Steam reforming stands as the primary industrial technique for generating Synthesis Gas (syngas) utilized in the production of hydrogen, green ammonia, and methanol. Nonetheless, the steam reforming process is associated with notable carbon dioxide emissions despite its various advantages.
This procedure entails the direct interaction of steam (H2O) and methane (CH4) using a catalyst under high pressures (20–40 bar) and temperatures (700–1100 °C). This results in the formation of synthesis gas (syngas), which is subsequently blended with nitrogen (N2) to produce ammonia (NH3). SMR is an exceptionally efficient process that optimizes the heat and chemical energy of the reactants. Moreover, it offers a cost-effective approach, making it the most economically viable method for the production of blue ammonia, which, in turn, is propelling revenue growth within this segment.
In the global blue ammonia market, the electrochemical process segment is anticipated to hold a notably substantial portion of the revenue during the forecast period. The preference for electrochemical methods over alternatives like the Haber-Bosch process is on the rise. The Haber-Bosch process has drawbacks, chiefly its high energy demand due to reliance on elevated temperatures and pressures. Moreover, it is environmentally unsustainable and detrimental, as it relies on nonrenewable hydrogen feedstock, highlighting the necessity for greener alternatives.
In contrast, the electrochemical approach offers multiple advantages. It enables ammonia production at ambient temperature and pressure while utilizing water as a proton source. When compared to the Haber-Bosch process, this method often requires less energy, proves to be more cost-effective, and has a reduced adverse impact on the environment. These merits are driving the revenue growth of the electrochemical process segment.
By Technology Analysis
- The AutoThermal Reforming (ATR) segment accounted for the highest market share during the forecast period
ATR is gaining prominence as an appealing choice for upcoming blue hydrogen projects, particularly when seamlessly integrated with carbon capture technology, due to its numerous advantages. Key players in the chemical and energy industries, such as Air Liquide, Equinor, Air Products, and others, are actively adopting ATR for large-scale blue hydrogen facilities.
The ATR process involves the direct amalgamation of methane and oxygen (O2) with the aid of a catalyst under high pressures (20–40 bar) and elevated temperatures (800–1000 °C). Following this, nitrogen is introduced into the resulting syngas to facilitate ammonia production. Although ATR consumes more energy compared to SMR, it excels in energy utilization efficiency. Furthermore, it yields a higher volume of ammonia in comparison to SMR, enhancing overall process efficiency and enabling comprehensive carbon capture, thereby driving revenue growth in this segment.
Regional Insights
- North America dominated the largest market in 2022
In the global blue ammonia market, the North American region is poised to secure the largest share of revenue throughout the forecast period. This dominance can be attributed to the proactive efforts of key market players within this region who are actively engaged in the development of various infrastructures for blue ammonia production.
For instance, on February 6, 2023, Linde successfully entered into a lasting contract to provide environmentally friendly hydrogen and various industrial gases to OCI's expansive blue ammonia plant situated in Beaumont, Texas. Linde will take charge of managing the construction, ownership, and operation of an on-site complex, which will encompass a substantial air separation plant and incorporate auto-thermal reforming with carbon capture. This state-of-the-art facility will be seamlessly integrated into Linde's extensive industrial gas infrastructure within the Gulf Coast region.
The Asia Pacific market is set to experience the swiftest revenue growth rate in the global blue ammonia market during the forecast period. Japan, in particular, has emerged as a leader in electronic technology, largely attributable to its substantial efforts in advancing connector technologies.
In contrast to other nations, Japan has consistently achieved remarkable progress in ammonia procurement technology through extensive, long-term development initiatives, resulting in numerous advantages. As an illustration, on May 31, 2021, North American midstream company Pembina inked an agreement with one of Japan's largest trading firms to establish an end-to-end blue ammonia supply chain, connecting Western Canada's ammonia production to Japan and other Asian markets.
Anticipated outcomes include the production of up to 185,000 metric tons per year of blue hydrogen, which will subsequently be converted into 1 million metric tons per year of low-carbon ammonia. Furthermore, the facility will implement carbon capture technology to curtail CO2 emissions significantly.
Key Market Players & Competitive Insights
The market is characterized by intense competition, with established players relying on advanced technology, high-quality products, and a strong brand image to drive revenue growth. These companies employ various strategies such as research and development, mergers and acquisitions, and technological innovations to expand their product portfolios and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Some of the major players operating in the global market include:
- Air Liquide S.A.
- Ammonia Casale S.A.
- CF Industries Holdings, Inc.
- Haldor Topsoe A/S
- Linde ple
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd
- Siemens Energy AG
- TechnipFMC ple
- thyssenkrupp AG
- Yara International ASA
Recent Developments
- In June 2023, Yara International ASA and BASF have joined forces to create and construct a large-scale, low-carbon blue ammonia production plant with carbon capture in the Gulf Coast area of the United States. In response to the growing global need for low-carbon ammonia, the companies are exploring the potential for a facility with an overall capacity ranging from 1.2 to 1.4 million tons per year.
- In April 2023, through a collaborative endeavor encompassing various participants along the low-carbon ammonia value chain, Saudi Aramco effectively delivered the inaugural consignment of blue ammonia to Japan. SABIC Agri-Nutrients utilized Aramco's feedstock to produce the ammonia, which was subsequently procured by Fuji Oil Company through Aramco Trading Company. The responsibility for transporting the liquid to Japan was entrusted to Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, where the ammonia was then transferred.
- In March 2023, Linde plc, a renowned worldwide provider of industrial gases and engineering solutions, and OCI, a global manufacturer and supplier of hydrogen-based products, have entered into a long-term agreement. This arrangement entails Linde's provision of clean hydrogen and nitrogen to OCI's upcoming blue ammonia facility, currently under development in Texas, USA.
- In December 2022, OCI has announced its plans to build the largest blue ammonia facility in Texas. The project is wholly owned by OCI and is estimated to necessitate an investment of approximately USD 1 billion. This budget encompasses the costs associated with expanded utilities and available land, enabling the potential for doubling the facility's capacity to 2.2 million metric tons per annum in the future.
Blue Ammonia Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2024 |
USD 14.51 million |
|
Revenue forecast in 2032 |
USD 22.91 million |
|
CAGR |
5.90% from 2024 – 2032 |
|
Base year |
2023 |
|
Historical data |
2019 – 2022 |
|
Forecast period |
2024 – 2032 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2024 to 2032 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Technology, By Manufacturing process, By Distribution Channel, By Application, By End-Use, By Region |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, region, and segmentation. |
